Direct diagnosis of human respiratory coronaviruses 229E and OC43 by the polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 11483217
- PMCID: PMC7119936
- DOI: 10.1016/s0166-0934(01)00343-3
Direct diagnosis of human respiratory coronaviruses 229E and OC43 by the polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
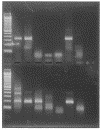
An RT-PCR-hybridization was developed that amplified genetic material from the M protein gene of HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43. The analytic sensitivity of these original primers were compared with primers defined in the N gene and described previously. The results show that 0.05 TCID50 of HCoV-229E and 0.01 TCID50 of HCoV-OC43 can be detected by this molecular method using the original method. Detection of HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43 in clinical specimens is possible using this method: 348 respiratory specimens (202 sputum and 146 nasal aspirates) were tested with this RT-PCR-hybridization and 12 human coronavirus are detected (3%). The method could provide a useful tool for demonstrating the role of human coronavirus in infections of the respiratory tract.
Figures
References
-
- Cantaloube J.F., Charrel R.N., Attoui H., Biagini P., De Micco P., De Lamballerie X. Evaluation of four PCR sustems amplifying different genomic regions for molecular diagnosis of GB virus C infections. J. Virol. Methods. 1997;64:131–135. - PubMed
-
- Freymuth F., Quibriac M., Petitjean J., Daon F., Amiel M.L. Les virus responsables d'infections respiratoires en pédiatrie. Bilan de 3480 aspirations nasales réalisées chez l'enfant sur une période de six ans. Ann. Pédiatr. 1987;34:493–501. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

