Cell surface monoamine oxidases: enzymes in search of a function
- PMID: 11483492
- PMCID: PMC149172
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.15.3893
Cell surface monoamine oxidases: enzymes in search of a function
Abstract
Ectoenzymes with a catalytically active domain outside the cell surface have the potential to regulate multiple biological processes. A distinct class of copper-containing semicarbazide-sensitive monoamine oxidases, expressed on the cell surface and in soluble forms, oxidatively deaminate primary amines. Via transient covalent enzyme-substrate intermediates, this reaction results in production of aldehydes, hydrogen peroxide and ammonium, which are all biologically active substances. The physiological functions of these enzymes have remained unknown, although they have been suggested to be involved in the metabolism of biogenic amines. Recently, new roles have been proposed for these enzymes in regulation of glucose uptake and, even more surprisingly, in leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions. The emerging functions of ectoenzymes in signalling and cell-cell adhesion suggest a novel mode of molecular control of these complex processes.
Figures



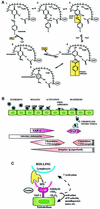
References
-
- Bogdan C., Röllinghoff,M. and Diefenbach,A. (2000) Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 12, 64–76. - PubMed
-
- Bono P., Salmi,M., Smith,D.J. and Jalkanen,S. (1998a) Cloning and characterization of mouse vascular adhesion protein-1 reveals a novel molecule with enzymatic activity. J. Immunol., 160, 5563–5571. - PubMed
-
- Bono P., Salmi,M., Smith,D.J., Leppänen,I., Horelli-Kuitunen,N., Palotie,A. and Jalkanen,S. (1998b) Isolation, structural characterization and chromosomal mapping of the mouse vascular adhesion protein-1 gene and promoter. J. Immunol., 161, 2953–2960. - PubMed
-
- Boomsma F., van Dijk,J., Bhaggoe,U.M., Bouhuizen,A.M. and van den Meiracker,A.H. (2000) Variation in semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase activity in plasma and tissues of mammals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 126, 69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

