Propagation of the apoptotic signal by mitochondrial waves
- PMID: 11483514
- PMCID: PMC149166
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.15.4107
Propagation of the apoptotic signal by mitochondrial waves
Abstract
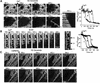
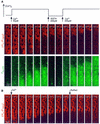
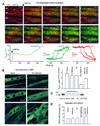
Generation of mitochondrial signals is believed to be important in the commitment to apoptosis, but the mechanisms coordinating the output of individual mitochondria remain elusive. We show that in cardiac myotubes exposed to apoptotic agents, Ca2+ spikes initiate depolarization of mitochondria in discrete subcellular regions, and these mitochondria initiate slow waves of depolarization and Ca2+ release propagating through the cell. Traveling mitochondrial waves are prevented by Bcl-x(L), involve permeability transition pore (PTP) opening, and yield cytochrome c release, caspase activation and nuclear apoptosis. Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake is critical for wave propagation, and mitochondria at the origin of waves take up Ca2+ particularly effectively, providing a mechanism that may underlie selection of the initiation sites. Thus, apoptotic agents transform the mitochondria into an excitable state by sensitizing PTP to Ca2+. Expansion of the local excitation by mitochondrial waves propagating through the whole cell can be especially important in activation of the apoptotic machinery in large cells.
Figures






References
-
- Alnemri E.S. (1999) Hidden powers of the mitochondria. Nature Cell Biol., 1, 40–42. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi P., Scorrano,L., Colonna,R., Petronilli,V. and Di Lisa,F. (1999) Mitochondria and cell death. Mechanistic aspects and methodological issues. Eur. J. Biochem., 264, 687–701. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J. (1997) The AM and FM of calcium signalling. Nature, 386, 759–760. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J., Bootman M.D. and Lipp,P. (1998) Calcium—a life and death signal. Nature, 395, 645–648. - PubMed
-
- Bers D.M. (1991) Excitation–Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 1–258.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

