Measurement of chloride flux associated with the myogenic response in rat cerebral arteries
- PMID: 11483706
- PMCID: PMC2278745
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00753.x
Measurement of chloride flux associated with the myogenic response in rat cerebral arteries
Abstract
1. Self-referencing ion-selective (SERIS) electrodes were used to measure the temperature and pressure dependence of Cl(-) efflux, during myogenic contraction of pressurized rat cerebral resistance arteries. 2. At room temperature (18-21 degrees C), a small, pressure-independent Cl(-) efflux was measured. On warming to 37 degrees C, arteries developed pressure-dependent myogenic tone, and this was associated with a pressure-dependent increase in Cl(-) efflux (n = 5). 3. Both myogenic tone and the pressure- and temperature-dependent Cl(-) efflux were abolished on application of 10 microM tamoxifen, a Cl(-) channel blocker (IC(50) 3.75 +/- 0.2 microM). Tamoxifen (10 microM) also prevented contraction to 60 mM K(+), suggesting non-specific effects of tamoxifen (n = 5). 4. Myogenic tone was abolished by 2 microM nimodipine, but Cl(-) efflux was unaffected. In the presence of nimodipine, 10 microM tamoxifen still abolished pressure- and temperature-dependent Cl(-) efflux (n = 3). 5. In summary, a Cl(-) efflux can be measured from rat cerebral arteries, with a temperature dependence that is closely correlated with myogenic contraction. We conclude that Cl(-) efflux through Cl(-) channels contributes to the depolarization associated with myogenic contraction.
Figures
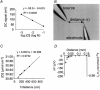
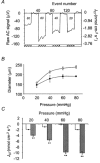
 ) was significant, when compared with measurements at the equivalent flux at 18-21 °C (□) at each pressure. **P < 0.01(n = 5).
) was significant, when compared with measurements at the equivalent flux at 18-21 °C (□) at each pressure. **P < 0.01(n = 5).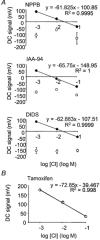
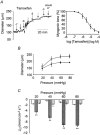
 ; 10 μ
; 10 μ ) (n = 4). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, compared to control at 18-21 °C.
) (n = 4). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, compared to control at 18-21 °C.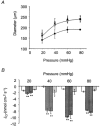
 ; 2 μ
; 2 μ ; 2 μ
; 2 μ ) (n = 4). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, compared to control at 18-21 °C.
) (n = 4). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, compared to control at 18-21 °C.References
-
- Aickin CC. Chloride transport across the sarcolemma of vertebrate smooth and skeletal muscle. In: Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Russel JM, editors. Chloride Channels and Carriers in Nerve, Muscle and Glial Cells. New York: Plenum Press; 1990. pp. 209–249.
-
- Ammann D. In: Ion-selective Microelectrodes: Principles, Design and Application. Ammann D, editor. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1986.
-
- Brayden JE, Nelson MT. Regulation of arterial tone by activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels. Science. 1992;256:532–535. - PubMed
-
- Brayden JE, Quayle JM, Standen NB, Nelson MT. Role of potassium channels in the vascular response to endogenous and pharmacological vasodilators. Blood Vessels. 1991;28:147–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

