Spermatogenesis and the regulation of Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV localization are not dependent on calspermin
- PMID: 11486043
- PMCID: PMC87323
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.17.6066-6070.2001
Spermatogenesis and the regulation of Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV localization are not dependent on calspermin
Abstract
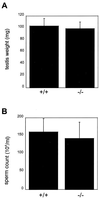
Calspermin and Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV) are two proteins encoded by the Camk4 gene. CaMKIV is found in multiple tissues, including brain, thymus, and testis, while calspermin is restricted to the testis. In the mouse testis, both proteins are expressed within elongating spermatids. We have recently shown that deletion of CaMKIV has no effect on calspermin expression but does impair spermiogenesis by disrupting the exchange of sperm basic nuclear proteins. The function of calspermin within the testis is unclear, although it has been speculated to play a role in binding and sequestering calmodulin during the development of the germ cell. To investigate the contribution of calspermin to spermatogenesis, we have used Cre/lox technology to specifically delete calspermin, while leaving kinase expression intact. We unexpectedly found that calspermin is not required for male fertility. We further demonstrate that CaMKIV expression and localization are unaffected by the absence of calspermin and that calspermin does not colocalize to the nuclear matrix with CaMKIV.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV is expressed in spermatids and targeted to chromatin and the nuclear matrix.J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 17;275(11):7994-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.11.7994. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10713118
-
Spermiogenesis and exchange of basic nuclear proteins are impaired in male germ cells lacking Camk4.Nat Genet. 2000 Aug;25(4):448-52. doi: 10.1038/78153. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 10932193
-
Regulation and properties of the rat Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV gene and its protein products.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:389-406; discussion 406-7. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997. PMID: 9238860 Review.
-
Calspermin gene transcription is regulated by two cyclic AMP response elements contained in an alternative promoter in the calmodulin kinase IV gene.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):561-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.1.561. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7799965 Free PMC article.
-
Calspermin: a 32K-dalton calmodulin-binding protein in central nervous system and male reproductive system; property and distribution.Cell Calcium. 1986 Dec;7(5-6):329-38. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90036-9. Cell Calcium. 1986. PMID: 3028637 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of genome-wide SNP-SNP interactions associated with important traits in chicken.BMC Genomics. 2017 Nov 21;18(1):892. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4252-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29162033 Free PMC article.
-
Differential venom gland gene expression analysis of juvenile and adult scorpions Androctonus crassicauda.BMC Genomics. 2022 Sep 8;23(1):636. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08866-1. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36076177 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-dependent kinase IV links Toll-like receptor 4 signaling with survival pathway of activated dendritic cells.Blood. 2008 Jan 15;111(2):723-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-091173. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Blood. 2008. PMID: 17909078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blendy J A, Kaestner K H, Weinbauer G F, Nieschlag E, Schutz G. Severe impairment of spermatogenesis in mice lacking the CREM gene. Nature. 1996;380:162–165. - PubMed
-
- Epstein P N, Christenson M A, Means A R. Chicken calmodulin promoter activity in proliferating and differentiated cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989;3:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Fimia G M, De Cesare D, Sassone-Corsi P. CBP-independent activation of CREM and CREB by the LIM-only protein ACT. Nature. 1999;398:165–169. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes N S, Mellstrom B, Benusiglio E, Sassone-Corsi P. Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator. Nature. 1992;355:80–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
