A dominant negative inhibitor of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors suppresses cerebellar granule cell apoptosis by blocking c-Jun activation
- PMID: 11487612
- PMCID: PMC6763154
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-05893.2001
A dominant negative inhibitor of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors suppresses cerebellar granule cell apoptosis by blocking c-Jun activation
Abstract
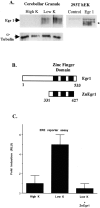
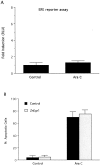
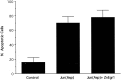
To investigate the role of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors in neuronal apoptosis, we examined the effect of a dominant negative Egr inhibitor construct in a well characterized in vitro paradigm, cerebellar granule cell death induced by withdrawal of depolarizing concentrations of extracellular potassium. We found that this apoptotic stimulus increases the activity of a reporter gene driven by the Egr response element and that a dominant negative inhibitor of Egr-mediated transcription blocks granule cell apoptosis. In contrast, apoptosis of immature granule cells induced by cytosine arabinoside is not inhibited by the Egr inhibitor construct. Because activation of c-Jun is an essential step in granule cell death induced by potassium deprivation, but not cytosine arabinoside, we asked whether the Egr inhibitor acts by influencing c-Jun activation or its ability to induce apoptosis. We found that the Egr inhibitor does not block the ability of a constitutively active c-Jun construct to induce apoptosis in these cells but does suppress activation of c-Jun-mediated transcription induced by lowering extracellular potassium concentration. Furthermore, the Egr inhibitor blocks the ability of MEKK1 [mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase kinase 1], an upstream kinase capable of stimulating the JNK (c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase)-c-Jun pathway, to induce apoptosis and activate c-Jun. Together, these studies indicate that the Egr family of transcription factors plays a critical role in neuronal apoptosis and identify c-Jun activation as an important downstream target of the Egr family in this process.
Figures



References
-
- Ahn S, Ginty DD, Linden DJ. A late phase of cerebellar long-term depression requires activation of CaMKIV and CREB. Neuron. 1999;23:559–568. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner EF. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
-
- Catania MV, Copani A, Calogero A, Ragonese GI, Condorelli DF, Nicoletti F. An enhanced expression of the immediate early gene, Egr-1, is associated with neuronal apoptosis in culture. Neuroscience. 1999;91:1529–1538. - PubMed
-
- Chapman NR, Perkins ND. Inhibition of the RelA(p65) NF-kappaB subunit by Egr-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:4719–4724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
