Paradoxical role of large-conductance calcium-activated K+ (BK) channels in controlling action potential-driven Ca2+ entry in anterior pituitary cells
- PMID: 11487613
- PMCID: PMC6763171
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-05902.2001
Paradoxical role of large-conductance calcium-activated K+ (BK) channels in controlling action potential-driven Ca2+ entry in anterior pituitary cells
Abstract
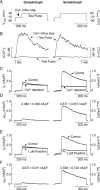
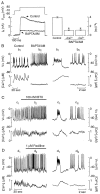
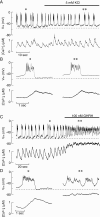
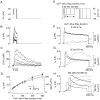
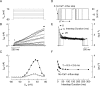
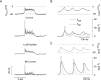
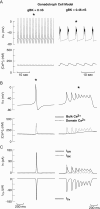
Activation of high-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels normally limits action potential duration and the associated voltage-gated Ca(2+) entry by facilitating membrane repolarization. Here we report that BK channel activation in rat pituitary somatotrophs prolongs membrane depolarization, leading to the generation of plateau-bursting activity and facilitated Ca(2+) entry. Such a paradoxical role of BK channels is determined by their rapid activation by domain Ca(2+), which truncates the action potential amplitude and thereby limits the participation of delayed rectifying K(+) channels during membrane repolarization. Conversely, pituitary gonadotrophs express relatively few BK channels and fire single spikes with a low capacity to promote Ca(2+) entry, whereas an elevation in BK current expression in a gonadotroph model system leads to the generation of plateau-bursting activity and high-amplitude Ca(2+) transients.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fast-activating voltage- and calcium-dependent potassium (BK) conductance promotes bursting in pituitary cells: a dynamic clamp study.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 16;31(46):16855-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3235-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22090511 Free PMC article.
-
Role of BK potassium channels shaping action potentials and the associated [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations in GH(3) rat anterior pituitary cells.Neuroendocrinology. 2003 Mar;77(3):162-76. doi: 10.1159/000069509. Neuroendocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12673050
-
Activation of BK channels in rat chromaffin cells requires summation of Ca(2+) influx from multiple Ca(2+) channels.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Sep;84(3):1123-35. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.3.1123. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10979988
-
Calcium-activated potassium channels in adrenal chromaffin cells.Ion Channels. 1996;4:261-301. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1775-1_7. Ion Channels. 1996. PMID: 8744211 Review.
-
Biophysical basis of pituitary cell type-specific Ca2+ signaling-secretion coupling.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005 May-Jun;16(4):152-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.03.003. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15860411 Review.
Cited by
-
Large conductance voltage-and calcium-activated K+ (BK) channel in health and disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 22;15:1373507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373507. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38584598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons from models of pancreatic beta cells for engineering glucose-sensing cells.Math Biosci. 2010 Sep;227(1):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 24. Math Biosci. 2010. PMID: 20580727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast-activating voltage- and calcium-dependent potassium (BK) conductance promotes bursting in pituitary cells: a dynamic clamp study.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 16;31(46):16855-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3235-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22090511 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic activation of BK currents in vivo generates bidirectional effects on neuronal excitability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 13;109(46):18997-9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205573109. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23112153 Free PMC article.
-
slo K(+) channel gene regulation mediates rapid drug tolerance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17276-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405584101. Epub 2004 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15569939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araque A, Buno W. Fast BK-type channel mediates the Ca2+-activated K+ current in crayfish muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:1655–1661. - PubMed
-
- Barry PH. JPCalc, a software package for calculating liquid junction potential corrections in patch-clamp, intracellular, epithelial, and bilayer measurements. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;51:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Behrens R, Nolting A, Reimann F, Schwarz M, Waldschutz R, Pongs O. HKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4, cloning and characterization of two members of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel β-subunit family. FEBS Lett. 2000;474:99–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
