Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 accelerates NMDA receptor trafficking
- PMID: 11487629
- PMCID: PMC6763135
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-06058.2001
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 accelerates NMDA receptor trafficking
Abstract
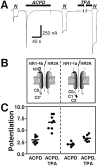
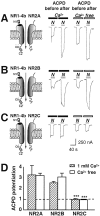
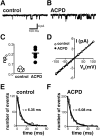
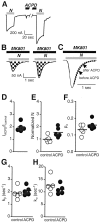
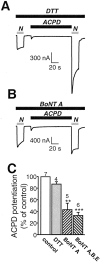
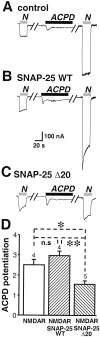
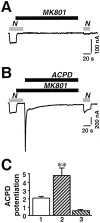
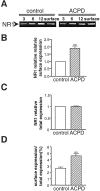
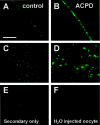
Regulation of neuronal NMDA receptors (NMDARs) by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) is known to play a critical role in synaptic transmission. The molecular mechanisms underlying mGluR1-mediated potentiation of NMDARs are as yet unclear. The present study shows that in Xenopus oocytes expressing recombinant receptors, activation of mGluR1 potentiates NMDA channel activity by recruitment of new channels to the plasma membrane via regulated exocytosis. Activation of mGluR1alpha induced (1) an increase in channel number times channel open probability, with no change in mean open time, unitary conductance, or reversal potential; (2) an increase in charge transfer in the presence of NMDA and the open channel blocker MK-801, indicating an increased number of functional NMDARs in the cell membrane; and (3) increased NR1 surface expression, as indicated by cell surface Western blots and immunofluorescence. Botulinum neurotoxin A or expression of a dominant negative mutant of synaptosomal associated protein of 25 kDa molelcular mass (SNAP-25) greatly reduced mGluR1alpha-mediated potentiation, indicating that receptor trafficking occurs via a SNAP-25-mediated form of soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor-dependent exocytosis. Because group I mGluRs are localized to the perisynaptic region in juxtaposition to synaptic NMDARs at glutamatergic synapses in the hippocampus, mGluR-mediated insertion of NMDARs may play a role in synaptic transmission and plasticity, including long-term potentiation.
Figures
References
-
- Aiba A, Chen C, Herrup K, Rosenmund C, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S. Reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation and context-specific deficit in associative learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell. 1994a;79:365–375. - PubMed
-
- Aiba A, Kano M, Chen C, Stanton ME, Fox GD, Herrup K, Zwingman TA, Tonegawa S. Deficient cerebellar long-term depression and impaired motor learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell. 1994b;79:377–388. - PubMed
-
- Akabas MH, Stauffer DA, Xu M, Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992;258:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Alagarsamy S, Marino MJ, Rouse ST, Gereau RW4, Heinemann SF, Conn PJ. Activation of NMDA receptors reverses desensitization of mGluR5 in native and recombinant systems. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Aniksztejn L, Otani S, Ben-Ari Y. Quisqualate metabotropic receptors modulate NMDA currents and facilitate induction of long-term potentiation through protein kinase C. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4:500–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
