Ducky mouse phenotype of epilepsy and ataxia is associated with mutations in the Cacna2d2 gene and decreased calcium channel current in cerebellar Purkinje cells
- PMID: 11487633
- PMCID: PMC6763162
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-06095.2001
Ducky mouse phenotype of epilepsy and ataxia is associated with mutations in the Cacna2d2 gene and decreased calcium channel current in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Abstract
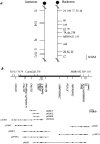
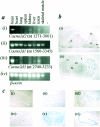
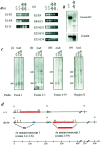
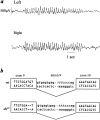
The mouse mutant ducky, a model for absence epilepsy, is characterized by spike-wave seizures and ataxia. The ducky gene was mapped previously to distal mouse chromosome 9. High-resolution genetic and physical mapping has resulted in the identification of the Cacna2d2 gene encoding the alpha2delta2 voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit. Mutations in Cacna2d2 were found to underlie the ducky phenotype in the original ducky (du) strain and in a newly identified strain (du(2J)). Both mutations are predicted to result in loss of the full-length alpha2delta2 protein. Functional analysis shows that the alpha2delta2 subunit increases the maximum conductance of the alpha1A/beta4 channel combination when coexpressed in vitro in Xenopus oocytes. The Ca(2+) channel current in acutely dissociated du/du cerebellar Purkinje cells was reduced, with no change in single-channel conductance. In contrast, no effect on Ca(2+) channel current was seen in cerebellar granule cells, results consistent with the high level of expression of the Cacna2d2 gene in Purkinje, but not granule, neurons. Our observations document the first mammalian alpha2delta mutation and complete the association of each of the major classes of voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channel subunits with a phenotype of ataxia and epilepsy in the mouse.
Figures


References
-
- Barclay J, Rees M. Genomic organisation of the mouse and human α2δ2 voltage dependent calcium channel subunit genes. Mamm Genome. 2000;11:1142–1144. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Lipp P. Calcium: a life and death signal. Nature. 1998;395:645–648. - PubMed
-
- Blatt C, Eversole-Cire P, Cohn VH, Zollman S, Fournier RE, Mohandas LT, Nesbitt M, Lugo T, Jones DT, Reed RR, Weiner LP, Sparkes RS, Simon MI. Chromosomal localization of genes encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunits in mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:7642–7646. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burgess DL, Jones JM, Meisler MH, Noebels JL. Mutation of the Ca2+ channel β subunit gene Cchb4 is associated with ataxia and seizures in the lethargic (lh) mouse. Cell. 1997;88:385–392. - PubMed
-
- Burgess DL, Biddlecombe GH, McDonough SI, Diaz ME, Zilinski CA, Bean BP, Campbell KP, Noebels JL. Beta subunit reshuffling modifies N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channel subunit compositions in lethargic mouse brain. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;13:293–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
