Quantitative analysis of synaptic contacts made between functionally identified oralis neurons and trigeminal motoneurons in cats
- PMID: 11487653
- PMCID: PMC6763181
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-06298.2001
Quantitative analysis of synaptic contacts made between functionally identified oralis neurons and trigeminal motoneurons in cats
Abstract
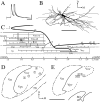
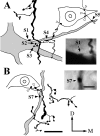
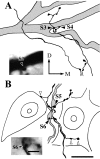
A previous study revealed that rostrodorsomedial oralis (Vo.r) neurons synapsing on trigeminal motoneurons use GABA and/or glycine as neurotransmitters. To determine the number and spatial distribution of contacts, injections of biotinamide and horseradish peroxidase were made into a Vo.r neuron and an alpha-motoneuron in the jaw-closing (JC) and jaw-opening (JO) motor nucleus, respectively, in 39 cats. All Vo.r neurons responded to low-threshold mechanical stimulation of the oral tissues. Single Vo.r neurons terminating in the JC nucleus (Vo.r-dl neurons; n = 5) issued, on average, 10 times more boutons than Vo.r neurons terminating in the JO nucleus (Vo.r-vm neurons; n = 5; 4437 vs 445). The Vo.r-dl neuron-JC alpha-motoneuron pairs (n = 4) made contacts on either the soma-dendritic compartment or dendrites, and the Vo.r-vm neuron-JO motoneuron pairs (n = 2) made contacts on dendrites, with a range of two to seven contacts. In five of the six pairs, individual or groups of two to three terminals contacted different dendritic branches of a postsynaptic cell. The Vo.r-dl neurons innervated a greater number of counter-stained motoneuronal somata than did the Vo.r-vm neurons (216 vs 26). Total number of contacts per Vo.r neuron was higher for the Vo.r-dl than Vo.r-vm neurons (786 vs 72). The present study demonstrates that axonal branches of Vo.r neurons are divided into two types with different innervation domains on the postsynaptic neuron and that they are highly divergent. The overall effect exerted by these neurons is predicted to be much greater within the JC than JO motoneuron pool.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Quantitative ultrastructure of physiologically identified premotoneuron terminals in the trigeminal motor nucleus in the cat.J Comp Neurol. 2000 Oct 9;426(1):13-30. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10980481
-
Serotonergic axonal contacts on identified cat trigeminal motoneurons and their correlation with medullary raphe nucleus stimulation.J Comp Neurol. 1997 Aug 4;384(3):443-55. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19970804)384:3<443::aid-cne9>3.0.co;2-3. J Comp Neurol. 1997. PMID: 9254038
-
Bilateral projection of functionally characterized trigeminal oralis neurons to trigeminal motoneurons in cats.Brain Res. 2005 Mar 2;1036(1-2):208-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.12.042. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15725420
-
Spatial distribution patterns of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the dendritic tree differ between jaw-closing and -opening motoneurons.Arch Oral Biol. 2007 Apr;52(4):321-4. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2006.11.003. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Arch Oral Biol. 2007. PMID: 17174264 Review.
-
Monitoring activity in neuronal populations with single-cell resolution in a behaving vertebrate.Histochem J. 1998 Mar;30(3):153-67. doi: 10.1023/a:1003243302777. Histochem J. 1998. PMID: 10188924 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrastructural analysis of low-threshold mechanoreceptive vibrissa afferent boutons in the cat trigeminal caudal nucleus.Anat Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;43(4):340-6. doi: 10.5115/acb.2010.43.4.340. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Anat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21267409 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of c-Fos immunoreactive brainstem neurons activated during fictive mastication in the rabbit.Exp Brain Res. 2005 Sep;165(4):478-89. doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-2319-5. Epub 2005 May 11. Exp Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15887006
-
Central connectivity of transient receptor potential melastatin 8-expressing axons in the brain stem and spinal dorsal horn.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 7;9(4):e94080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094080. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24710558 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic connectivity of the TRPV1-positive trigeminal afferents in the rat lateral parabrachial nucleus.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 30;17:1162874. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1162874. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37066077 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of the dendritic architectures of single jaw-closing and jaw-opening motoneurons in cats.Exp Brain Res. 2003 Jun;150(3):265-75. doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1458-9. Epub 2003 Apr 18. Exp Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12707745
References
-
- Arvidsson J, Gobel S. An HRP study of the central projections of primary trigeminal neurons which innervate tooth pulps in the cat. Brain Res. 1981;210:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Bae YC, Nakagawa S, Yabuta NH, Yoshida A, Pil PK, Moritani M, Chen K, Takemura M, Shigenaga Y. Electron microscopic observations of synaptic connections of jaw-muscle spindle and periodontal afferent terminals in the trigeminal motor and supratrigeminal nuclei in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1996;374:421–435. - PubMed
-
- Buhl EH, Halasy K, Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994;368:823–828. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Glenn LL. Horseradish peroxidase study of the spatial and electrotonic distribution of group Ia synapses on type-identified ankle extensor motoneurons in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1996;372:465–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
