Expression of Arabidopsis GAI in transgenic rice represses multiple gibberellin responses
- PMID: 11487693
- PMCID: PMC139124
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010020
Expression of Arabidopsis GAI in transgenic rice represses multiple gibberellin responses
Abstract
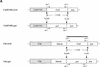
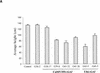
Bioactive gibberellins (GAs) are essential endogenous regulators of plant growth. GA signaling is mediated via GAI, a nuclear member of the GRAS family of plant transcription factors. Previous experiments have suggested that GAI is a GA-derepressible repressor of plant growth. Here we test this hypothesis by examining the effects of the expression of Arabidopsis GAI in transgenic Basmati rice. High-level expression of GAI caused dwarfism and reduced GA responses, and the strength of this effect was correlated with the level of transgene expression. In particular, the expression of GAI abolished the GA-mediated induction of rice aleurone alpha-amylase activity, thus implicating GAI orthologs in the well-characterized cereal aleurone GA response. The GA derepressible repressor model predicts that high-level expression of GAI should confer dwarfism, and these observations are consistent with this prediction.
Figures






References
-
- Bethke, P.C., Schuurink, R., and Jones, R.L. (1997). Hormonal signalling in cereal aleurone. J. Exp. Bot. 48, 1337–1356.
-
- Börner, A., Plaschke, J., Korzun, V., and Worland, A.J. (1996). The relationships between the dwarfing genes of wheat and rye. Euphytica 89, 69–75.
-
- Christou, P., Ford, T.L., and Kofron, M. (1991). Genotype-independent stable transformation of rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Bio/Technology 9, 957–962.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

