G2/M-phase-specific transcription during the plant cell cycle is mediated by c-Myb-like transcription factors
- PMID: 11487700
- PMCID: PMC139135
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010102
G2/M-phase-specific transcription during the plant cell cycle is mediated by c-Myb-like transcription factors
Erratum in
- Plant Cell 2001 Sep;13(9):2159
Abstract
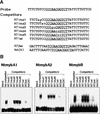
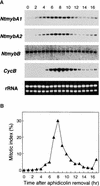
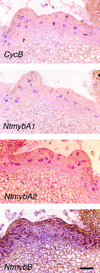
Plant B-type cyclin genes are expressed specifically in late G2- and M-phases during the cell cycle. Their promoters contain a common cis-acting element, called the MSA (M-specific activator) element, that is necessary and sufficient for periodic promoter activation. This motif also is present in the tobacco kinesin-like protein gene NACK1, which is expressed with timing similar to that of B-type cyclin genes. In this study, we show that G2/M-phase-specific activation of the NACK1 promoter also is regulated by the MSA element, suggesting that a defined set of G2/M-phase-specific genes are coregulated by an MSA-mediated mechanism. In a search for MSA binding factors by yeast one-hybrid screening, we identified three different Myb-like proteins that interact specifically with the MSA sequence. Unlike the majority of plant Myb-like proteins, these Myb proteins, NtmybA1, NtmybA2, and NtmybB, have three imperfect repeats in the DNA binding domain, as in animal c-Myb proteins. During the cell cycle, the level of NtmybB mRNA did not change significantly, whereas the levels of NtmybA1 and A2 mRNAs fluctuated and peaked at M-phase, when B-type cyclin genes were maximally induced. In transient expression assays, NtmybA1 and A2 activated the MSA-containing promoters, whereas NtmybB repressed them. Furthermore, expression of NtmybB repressed the transcriptional activation mediated by NtmybA2. Our data show that a group of plant Myb proteins that are structurally similar to animal c-Myb proteins have unexpected roles in G2/M-phase by modulating the expression of B-type cyclin genes and may regulate a suite of coexpressed genes.
Figures







References
-
- Albani, D., Mariconti, L., Ricagno, S., Pitto, L., Moroni, C., Helin, K., and Cella, R. (2000). DcE2F, a functional plant E2F-like transcriptional activator from Daucus carota. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 19258–19267. - PubMed
-
- Bilang, R., Klöti, A., Schrott, M., and Potrykus, I. (1994). PEG-mediated direct gene transfer and electroporation. In Plant Molecular Biology Manual, S.B. Gelvin and R.A. Schilperoort, eds (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers), pp. A1, 1–16.
-
- Black, A.R., and Azizkhan-Clifford, J. (1999). Regulation of E2F: A family of transcription factors involved in proliferation control. Gene 237, 281–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

