Adrenomedullin (ADM) in the human forearm vascular bed: effect of neutral endopeptidase inhibition and comparison with proadrenomedullin NH2-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP)
- PMID: 11488772
- PMCID: PMC2014526
- DOI: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.1420.x
Adrenomedullin (ADM) in the human forearm vascular bed: effect of neutral endopeptidase inhibition and comparison with proadrenomedullin NH2-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP)
Abstract
Aims: To compare the haemodynamic responses of proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) and adrenomedullin (ADM) in the forearm vascular bed of healthy male volunteers, and to investigate the role of neutral endopeptidase (NEP) in the metabolism of ADM.
Methods: On two separate occasions, ADM (1-30 pmol x min(-1)) and PAMP (100-3000 pmol x min(-1)) were infused into the brachial artery of eight male subjects, and forearm blood flow (FBF) assessed using venous occlusion plethysmography. In a second study, eight male subjects received the same doses of ADM, co-infused with either the NEP inhibitor thiorphan (30 nmol x min(-1)) or the control vasoconstrictor noradrenaline (120 pmol x min(-1)), on separate occasions. Both studies were conducted in a double-blind, randomized manner.
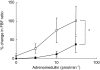
Results: ADM and PAMP produced a dose-dependent increase in FBF (P < or = 0.002). Based on the dose producing a 50% increase in FBF, ADM was approximately 60 times more potent than PAMP. Thiorphan and noradrenaline produced similar reductions in FBF of 14 +/- 4% (mean +/- s.e. mean) and 22 +/- 6%, respectively (P = 0.4). However, the area under the dose-response curve was significantly greater during co-infusion of ADM with thiorphan than with noradrenaline (P = 0.028), as was the maximum increase in FBF ratio (2.1 +/- 1.0 vs 1.2 +/- 0.2; P = 0.030).
Conclusions: ADM and PAMP both produce a local dose-related vasodilatation in the human forearm, but PAMP is approximately 60 times less potent than ADM. In addition, NEP inhibition potentiates the haemodynamic effects of ADM. These findings suggest that PAMP may not play a role in the physiological regulation of blood flow. However, in pathophysiological conditions such as hypertension and heart failure, NEP inhibition may exert a beneficial effect by increasing the biological activity of ADM.
Figures

References
-
- Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, et al. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Ishiyama Y, et al. Identification and hypotensive activity of proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) FEBS Lett. 1994;351:35–37. - PubMed
-
- Richards AM, Nicholls MG, Lewis L, Lainchbury JG. Adrenomedullin. Clin Sci. 1996;91:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Cheung B, Leung R. Elevated plasma levels of human adrenomedullin in cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic and renal disorders. Clin Sci. 1997;92:59–62. - PubMed
-
- Taniyama M, Kitamura K, Ban Y, Sugita E, Ito K, Katagiri T. Elevation of circulating proadrenomedullin N, terminal 20-peptide in thyrotoxicosis. Clin Endocrinol. 1997;46:271–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

