Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy: decrease in regional cerebral blood volume in hyperintense subcortical lesions inversely correlates with disability and cognitive performance
- PMID: 11498413
- PMCID: PMC7975190
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy: decrease in regional cerebral blood volume in hyperintense subcortical lesions inversely correlates with disability and cognitive performance
Abstract
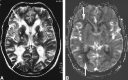
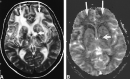
Background and purpose: Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is an arteriopathic syndrome related to a genetic defect on chromosome 19. Characteristic changes in CADASIL can be observed onT2-weighted MR images in the subcortical white matter. The purpose of this study was to measure changes of regional cerebral blood volume (rCBV) with dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and to correlate the changes to disability and cognitive performance.
Methods: We obtained rCBV measurements of 24 individuals with proven CADASIL on a 1.5-T MR imaging unit. A susceptibility-weighted MR imaging sequence was used for bolus tracking. Principles of the indicator dilution theory were applied to estimate values of absolute rCBV (mL/100 g). Disability was determined by using the Rankin scale, and overall cognitive performance was assessed by using the Mini-Mental State Examination.
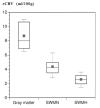
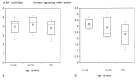
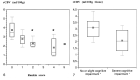
Results: The mean rCBV in the subcortical white matter that was hyperintense on the T2-weighted images (2.7 +/- 0.8 mL/100 g) was significantly lower than the rCBV in the white matter that appeared normal on the T2-weighted images (4.4 +/- 1.3 mL/100 g) (P <.05). The mean rCBV in the gray matter was within the normal range (8.3 +/- 1.7 mL/100 g). Both cognitive impairment and disability negatively correlated with rCBV in the subcortical white matter that was hyperintense (P <.05) but not with rCBV in the normal appearing white matter. rCBV did not correlate with age.
Conclusion: rCBV measured in the hyperintense subcortical white matter in individuals with CADASIL was decreased and inversely correlated with disability and cognitive impairment.
Figures
References
-
- Chabriat H, Vahedi K, Iba-Zizen MT, et al. Clinical spectrum of CADASIL: a study of 7 families: cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Lancet 1995;346:934-939 - PubMed
-
- Tournier-Lasserve E, Iba-Zizen MT, Romero N, Bousser MG. Autosomal dominant syndrome with strokelike episodes and leukoencephalopathy. Stroke 1991;22:1297-1302 - PubMed
-
- Tournier-Lasserve E, Joutel A, Melki J, et al. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy maps to chromosome 19ql2. Nat Genet 1993;3:256-259 - PubMed
-
- Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, et al. Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature 1996;383:707-710 - PubMed
-
- Joutel A, Vahedi K, Corpechot C, et al. Strong clustering and stereotyped nature of Notch3 mutations in CADASIL patients. Lancet 1997;350:1511-1515 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
