Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare cause of hypervascular nasal tumor
- PMID: 11498434
- PMCID: PMC7975225
Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare cause of hypervascular nasal tumor
Abstract
Cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma, first described in 1972, is an aggressive disease usually occurring in sun-exposed skin. Other sites have been described, however; such tumors occasionally occur within the nasal fossa. A high rate of metastasis (>30%) explains the poor prognosis. Descriptions of the imaging features of these tumors, mainly located in cutaneous region, are rare. We therefore present the imaging features of two cases of Merkel cell carcinoma involving the sinonasal region, suggestive of a hypervascular tumor.
Figures
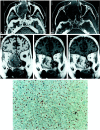
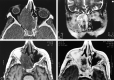
Similar articles
-
[Merkel cell carcinoma. A rare differential keratoacanthoma diagnosis].HNO. 1997 May;45(5):398-400. HNO. 1997. PMID: 9265025 German.
-
Unusual presentation of a Merkel cell carcinoma.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Feb;42(2 Pt 2):366-70. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(00)90114-2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10640935 Review.
-
Vascular density has prognostic value in Merkel cell carcinoma.Am J Dermatopathol. 2008 Oct;30(5):442-5. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e318172364d. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008. PMID: 18806485
-
Cytopathologic features of olfactory neuroblastoma.Cancer. 2006 Apr 25;108(2):86-92. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21718. Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16456848
-
Merkel cell carcinoma: a primer for the radiologist.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 Jun;200(6):1186-96. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.9884. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013. PMID: 23701052 Review.
Cited by
-
Merkel Cell Carcinoma of the Maxillary Sinus: An Unusual Presentation of a Common Tumor.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Jun;15(2):691-697. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01219-y. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32915383 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: An Otolaryngological Point of View of An Unusual Sinonasal Mass.Cureus. 2022 Nov 19;14(11):e31676. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31676. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36545167 Free PMC article.
-
Approach to intensely enhancing neck nodes.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2016 Mar-Apr;22(2):168-72. doi: 10.5152/dir.2015.14561. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26782154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma: a systematic review of ENT presentations.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Aug;270(8):2191-9. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-2283-1. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23192664
-
Imaging in patients with merkel cell carcinoma.J Skin Cancer. 2013;2013:973123. doi: 10.1155/2013/973123. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Skin Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23476783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Arch Dermatol 1972;105:107-110 - PubMed
-
- Camisa C, Weissman A. Friedrich Sigmund Merkel. Part II: the cell. Am J Dermatopathol 1982;4:527-535 - PubMed
-
- Tang C, Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin: an ultrastructural study. Cancer 1978;42:2311-2321 - PubMed
-
- Gu J, Polak JM, Van Noorden Pearse AGE, Marangos PJ, Azzopardi JC. Immunostaining of neuron specific enolase as a diagnostic tool for Merkel cell tumours. Cancer 1983;52:1039-1043 - PubMed
-
- Rice RD, Choukich GD, Thompson KS, Chase DR. Merkel cell tumor of the head and neck: five new cases with literature review. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;119:782-786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
