CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome
- PMID: 11498437
- PMCID: PMC7975191
CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome
Abstract
Eagle syndrome is an aggregate of symptoms caused by an elongated ossified styloid process, the cause of which remains unclear. This is a rare finding that often goes undetected in the absence of radiographic studies. In this case, we present the diagnostic CT and lateral view plain film radiography findings of a 39-year-old woman with clinical evidence of Eagle syndrome. Eagle syndrome can occur unilaterally or bilaterally and most frequently results in symptoms of dysphagia, headache, pain on rotation of the neck, pain on extension of the tongue, change in voice, and a sensation of hypersalivation (1, 2). We present rare and diagnostic radiographic evidence of this on both plain film radiographs and CT scans. Although well documented in otolaryngology literature and dentistry literature, this syndrome has not been reported in the radiology literature.
Figures
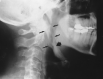
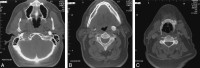
References
-
- Baugh RF, Stocks RM. Eagle's syndrome: a reappraisal. Ear Nose Throat J 1993;72:341-344 - PubMed
-
- Strauss M, Zohar Y, Laurian N. Elongated styloid process syndrome: intraoral versus external approach for styloid surgery. Laryngoscope 1979;95:976-979 - PubMed
-
- Balbuena L, Hayes D, Ramirez SG, Johnson R. Eagle's syndrome (elongated styloid process). South Med J 1997;90:331-334 - PubMed
-
- Rechtweg JS, Wax MK. Eagle's syndrome: a review. Am J Otolaryngol 1998;19:316-321 - PubMed
-
- Eagle WW. Elongated styloid process: symptoms and treatment. Arch Otolaryngol 1958;64:172-176 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
