Effects of homologues and analogues of palmitoylethanolamide upon the inactivation of the endocannabinoid anandamide
- PMID: 11498512
- PMCID: PMC1621151
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704199
Effects of homologues and analogues of palmitoylethanolamide upon the inactivation of the endocannabinoid anandamide
Abstract
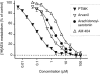
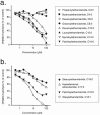
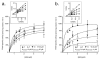
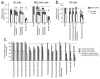
1. The ability of a series of homologues and analogues of palmitoylethanolamide to inhibit the uptake and fatty acid amidohydrolase (FAAH)-catalysed hydrolysis of [(3)H]-anandamide ([(3)H]-AEA) has been investigated. 2. Palmitoylethanolamide and homologues with chain lengths from 12 - 18 carbon atoms inhibited rat brain [(3)H]-AEA metabolism with pI(50) values of approximately 5. Homologues with chain lengths < or = eight carbon atoms gave < 20% inhibition at 100 microM. 3. R-palmitoyl-(2-methyl)ethanolamide, palmitoylisopropylamide and oleoylethanolamide inhibited [(3)H]-AEA metabolism with pI(50) values of 5.39 (competitive inhibition), 4.89 (mixed type inhibition) and 5.33 (mixed type inhibition), respectively. 4. With the exception of oleoylethanolamide, the compounds did not produce dramatic inhibition of [(3)H]-WIN 55,212-2 binding to human CB(2) receptors expressed on CHO cells. Palmitoylethanolamide, palmitoylisopropylamide and R-palmitoyl-(2-methyl)ethanolamide had modest effects upon [(3)H]-CP 55,940 binding to human CB(1) receptors expressed on CHO cells. 5. Most of the compounds had little effect upon the uptake of [(3)H]-AEA into C6 and/or RBL-2H3 cells. However, palmitoylcyclohexamide (100 microM) and palmitoylisopropylamide (30 and 100 microM) produced more inhibition of [(3)H]-AEA uptake than expected to result from inhibition of [(3)H]-AEA metabolism alone. 6. In intact C6 cells, palmitoylisopropylamide and oleoylethanolamide inhibited formation of [(3)H]-ethanolamine from [(3)H]-AEA to a similar extent as AM404, whereas palmitoylethanolamide, palmitoylcyclohexamide and R-palmitoyl-(2-methyl)ethanolamide were less effective. 7. These data provide useful information upon the ability of palmitoylethanolamide analogues to act as 'entourage' compounds. Palmitoylisopropylamide may prove useful as a template for design of compounds that reduce the cellular accumulation and metabolism of AEA without affecting either CB(1) or CB(2) receptors.
Figures


References
-
- ACKERMANN E.J., CONDE-FRIBOES K., DENNIS E.A. Inhibition of macrophage Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:445–450. - PubMed
-
- ALOE L., LEON A., LEVI-MOLTALCINI R. A proposed autacoid mechanism controlling mastocyte behaviour. Agents Actions. 1993;39:C145–C147. - PubMed
-
- BAKER D., PRYCE G., CROXFORD J.L., BROWN P., PERTWEE R.G., MAKRIYANNIS A., KHANOLKAR A., LAYWARD L., FEZZA F., BISOGNO T., DI MARZO V. Endocannabinoids control spasticity in a multiple sclerosis model. FASEB J. 2001;15:300–302. - PubMed
-
- BELTRAMO M., STELLA N., CALIGNANO A., LIN S.Y., MAKRIYANNIS A., PIOMELLI D. Functional role of high-affinity anandamide transport, as revealed by selective inhibition. Science. 1997;277:1094–1097. - PubMed
-
- BISOGNO T., MACCARRONE M., DE PETROCELLIS L., JARRAHIAN A., FINAZZI-AGRÒ A., HILLARD C., DI MARZO V. The uptake by cells of 2-arachidonoylglycerol, an endogenous agonist of cannabinoid receptors. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001;268:1982–1989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

