Translation initiation factor IF3: two domains, five functions, one mechanism?
- PMID: 11500382
- PMCID: PMC125572
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4560
Translation initiation factor IF3: two domains, five functions, one mechanism?
Abstract
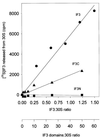
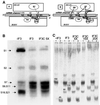
Initiation factor IF3 contains two domains separated by a flexible linker. While the isolated N-domain displayed neither affinity for ribosomes nor a detectable function, the isolated C-domain, added in amounts compensating for its reduced affinity for 30S subunits, performed all activities of intact IF3, namely: (i) dissociation of 70S ribosomes; (ii) shift of 30S-bound mRNA from 'stand-by' to 'P-decoding' site; (iii) dissociation of 30S-poly(U)-NacPhe-tRNA pseudo- initiation complexes; (iv) dissociation of fMet-tRNA from initiation complexes containing mRNA with the non-canonical initiation triplet AUU (AUUmRNA); (v) stimulation of mRNA translation regardless of its start codon and inhibition of AUUmRNA translation at high IF3C/ribosome ratios. These results indicate that while IF3 performs all its functions through a C-domain-30S interaction, the N-domain function is to provide additional binding energy so that its fluctuating interaction with the 30S subunit can modulate the thermodynamic stability of the 30S-IF3 complex and IF3 recycling. The localization of IF3C far away from the decoding site and anticodon stem-loop of P-site-bound tRNA indicates that the IF3 fidelity function does not entail its direct contact with these structures.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Initiation factor 3-induced structural changes in the 30 S ribosomal subunit and in complexes containing tRNA(f)(Met) and mRNA.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jun 9;299(3):615-28. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3774. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10835272
-
Translation of mRNAs with degenerate initiation triplet AUU displays high initiation factor 2 dependence and is subject to initiation factor 3 repression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4161-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4161. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8483930 Free PMC article.
-
A single mutation in the IF3 N-terminal domain perturbs the fidelity of translation initiation at three levels.J Mol Biol. 2008 Nov 28;383(5):937-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.012. Epub 2008 Sep 16. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18805426
-
Initiation of mRNA translation in bacteria: structural and dynamic aspects.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Nov;72(22):4341-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2010-3. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 30S ribosomal P site: a function of 16S rRNA.FEBS Lett. 2005 Feb 7;579(4):855-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.026. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15680962 Review.
Cited by
-
The antibiotic Furvina® targets the P-site of 30S ribosomal subunits and inhibits translation initiation displaying start codon bias.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov 1;40(20):10366-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks822. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22941660 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for an active role of IF3mt in the initiation of translation in mammalian mitochondria.Biochemistry. 2009 Apr 21;48(15):3269-78. doi: 10.1021/bi8023493. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19239245 Free PMC article.
-
The initiation factor 3 (IF3) residues interacting with initiator tRNA elbow modulate the fidelity of translation initiation and growth fitness in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 11;50(20):11712-11726. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1053. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36399509 Free PMC article.
-
Position of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF1 on the 40S ribosomal subunit determined by directed hydroxyl radical probing.Genes Dev. 2003 Nov 15;17(22):2786-97. doi: 10.1101/gad.1141803. Epub 2003 Nov 4. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14600024 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of helicases in translation initiation: a mechanistic view.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1829(8):799-809. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23337854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brandi A., Pietroni,P., Gualerzi,C.O. and Pon,C.L. (1996) Post-transcriptional regulation of CspA expression in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol., 19, 231–240. - PubMed
-
- Brombach M. and Pon,C. (1987) The unusual translational initiation codon AUU limits the expression of the infC (initiation factor IF3) gene of Escherichia coli.Mol. Gen. Genet., 208, 94–100. - PubMed
-
- Bruhns J. and Gualerzi,C. (1980) Structure–function relationship in Escherichia coli initiation factors: role of tyrosine residues in ribosomal binding and functional activity of IF-3. Biochemistry, 19, 1670–1676. - PubMed
-
- Calogero R.A., Pon,C.L. and Gualerzi,C.O. (1987) Chemical synthesis and in vivo hyperexpression of a modular gene coding for Escherichia coli translational initiation factor IF1. Mol. Gen. Genet., 208, 63–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

