Role of the heat shock protein 90 in immune response stimulation by bacterial DNA and synthetic oligonucleotides
- PMID: 11500428
- PMCID: PMC98668
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5546-5552.2001
Role of the heat shock protein 90 in immune response stimulation by bacterial DNA and synthetic oligonucleotides
Abstract
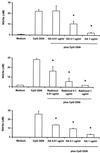
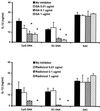
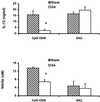
To elucidate the mechanisms of immunostimulation by bacterial DNA and synthetic oligonucleotides, the effects of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibitors on the activation of murine spleen cells and macrophages by these molecules were investigated. Murine spleen cells and J774 and RAW264.7 macrophages responded to a CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) and Escherichia coli DNA by increased production of interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-12, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and nitric oxide (NO). Pretreatment with any of the three Hsp90 inhibitors geldanamycin, radicicol, and herbimycin A resulted in a dose-dependent suppression of cytokine production from the spleen cells and macrophages and of NO from macrophages stimulated with CpG ODN or E. coli DNA. These Hsp90 inhibitors, however, had no effect on Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain 1-induced IL-12 production from either the murine spleen cells or macrophages. CpG ODN and E. coli DNA induced increased intracellular levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1 and -2), which are members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase family, while geldanamycin and radicicol blocked the phosphorylation of ERK1 and -2 in J774 and RAW264.7 cells. These data indicate that DNA-induced activation of murine spleen cells and macrophages is mediated by Hsp90 and that Hsp90 inhibitor suppression of DNA-induced macrophage activation is associated with disruption of the MAP kinase signaling pathway. Our findings suggest that Hsp90 inhibitors may provide a useful means of elucidating the mechanisms of immunostimulation by bacterial DNA and CpG ODN as well as a strategy for preventing adverse effects of bacterial DNA as well as lipopolysaccharide.
Figures


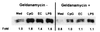

Similar articles
-
Role of Hsp90 in CpG ODN mediated immunostimulation in avian macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2010 Mar;47(6):1337-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.12.011. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20096933
-
The inhibitory action of sodium arsenite on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW 267.4 macrophage cells: a role of Raf-1 in lipopolysaccharide signaling.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 1;166(3):2011-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.3.2011. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160250
-
Requirement for a hsp90 chaperone-dependent MEK1/2-ERK pathway for B cell antigen receptor-induced cyclin D2 expression in mature B lymphocytes.J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 5;277(14):12144-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200102200. Epub 2002 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11823472
-
Phosphorothioate backbone modification modulates macrophage activation by CpG DNA.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 15;165(8):4165-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.8.4165. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11035048
-
Ras participates in CpG oligodeoxynucleotide signaling through association with toll-like receptor 9 and promotion of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 complex formation in macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):36334-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305698200. Epub 2003 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12867418
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori induces CCL20 expression.Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5223-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00731-07. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Infect Immun. 2007. Retraction in: Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):545. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01068-10. PMID: 17724069 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
CpG ODN activates NO and iNOS production in mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7).Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Jun;128(3):467-73. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01866.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12067301 Free PMC article.
-
Bench-to-bedside review: Toll-like receptors and their role in septic shock.Crit Care. 2002 Apr;6(2):125-36. doi: 10.1186/cc1471. Epub 2002 Feb 15. Crit Care. 2002. PMID: 11983038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Legionella pneumophila-induced interleukin-8 expression in human lung epithelial cells.BMC Microbiol. 2007 Nov 22;7:102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-102. BMC Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 18034886 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein inhibits herbimycin A-induced over-expression of inducible heat shock protein 70 kDa.Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Mar;245(1-2):191-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1022836616452. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12708759
References
-
- Becker J, Craig E A. Heat-shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Eur J Biochem. 1994;219:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Bird A P. Functions for DNA methylation in vertebrates. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Buchner J. Hsp90 & Co.—a holding for folding. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Chace J H, Hooker N A, Mildenstein K L, Krieg A M, Cowdery J S. Bacterial DNA-induced NK cell IFN-gamma production is dependent on macrophage secretion of IL-12. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997;84:185–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

