In vivo activation of dendritic cells and T cells during Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection
- PMID: 11500449
- PMCID: PMC98689
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5726-5735.2001
In vivo activation of dendritic cells and T cells during Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection
Abstract
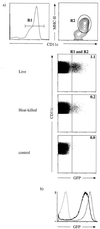
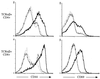
The present study was initiated to gain insight into the interaction between splenic dendritic cells (DC) and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in vivo. Splenic phagocytic cell populations associated with green fluorescent protein (GFP)-expressing bacteria and the bacterium-specific T-cell response were evaluated in mice given S. enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing GFP and ovalbumin. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that GFP-positive splenic DC (CD11c+ major histocompatibility complex class II-positive [MHC-II+] cells) were present following bacterial administration, and confocal microscopy showed that GFP-expressing bacteria were contained within CD11c+ MHC-II+ splenocytes. Furthermore, splenic DC and T cells were activated following Salmonella infection. This was shown by increased surface expression of CD86 and CD40 on CD11c+ MHC-II+ cells and increased CD44 and CD69 expression on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Salmonella-specific gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-producing cells in both of these T-cell subsets, as well as cytolytic effector cells, were also generated in mice given live bacteria. The frequency of Salmonella-specific CD4+ T cells producing IFN-gamma was greater than that of specific CD8+ T cells producing IFN-gamma in the same infected animal. This supports the argument that the predominant source of IFN-gamma production by cells of the specific immune response is CD4+ T cells. Finally, DC that phagocytosed live or heat-killed Salmonella in vitro primed bacterium-specific IFN-gamma-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as well as cytolytic effector cells following administration into naïve mice. Together these data suggest that DC are involved in priming naïve T cells to Salmonella in vivo.
Figures

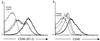



Similar articles
-
Antigen presentation capacity and cytokine production by murine splenic dendritic cell subsets upon Salmonella encounter.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;169(1):108-16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.108. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12077235
-
In vivo compartmentalization of functionally distinct, rapidly responsive antigen-specific T-cell populations in DNA-immunized or Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium-infected mice.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6390-400. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6390-6400.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501769 Free PMC article.
-
Role for inducible costimulator in control of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in mice.Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1050-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1050-1061.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428752 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella infection of bone marrow-derived macrophages and dendritic cells: influence on antigen presentation and initiating an immune response.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000 Apr;27(4):313-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2000.tb01445.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10727887 Review.
-
Antigen-presenting cells and anti-Salmonella immunity.Microbes Infect. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(14-15):1239-48. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01484-8. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11755412 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a system to study CD4+-T-cell responses to transgenic ovalbumin-expressing Toxoplasma gondii during toxoplasmosis.Infect Immun. 2004 Dec;72(12):7240-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7240-7246.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15557649 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an experimental model for liver abscess induction in Holstein steers using an acidotic diet challenge and bacterial inoculation.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae046. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae046. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38447078 Free PMC article.
-
An enteric pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium suppresses tumor growth by downregulating CD44high and CD4T regulatory (Treg) cell expression in mice: the critical role of lipopolysaccharide and Braun lipoprotein in modulating tumor growth.Cancer Gene Ther. 2010 Feb;17(2):97-108. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2009.58. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 19713997 Free PMC article.
-
Colonization and effector functions of innate lymphoid cells in mucosal tissues.Microbes Infect. 2016 Oct;18(10):604-614. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Microbes Infect. 2016. PMID: 27365193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two Salmonella OmpC K(b)-restricted epitopes for CD8+-T-cell recognition.Infect Immun. 2004 May;72(5):3059-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.3059-3062.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15102821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austyn J M, Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specificially against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981;11:805–815. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu Y J, Pulendran B, Palucka K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman R M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998;392:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Cobbold S P, Jayasuriya A, Nash A, Prospero T D, Waldmann H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984;312:548–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

