Effects of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection on regulation of L-arginine uptake and synthesis of reactive nitrogen intermediates in J774.1 murine macrophages
- PMID: 11500460
- PMCID: PMC98700
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5823-5831.2001
Effects of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection on regulation of L-arginine uptake and synthesis of reactive nitrogen intermediates in J774.1 murine macrophages
Abstract
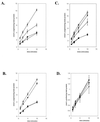
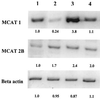
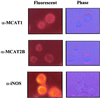
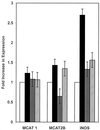
The generation of nitric oxide (NO) by activated macrophages is believed to control mycobacterial infection in the murine system. In this study we examined the effect of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection on the L-arginine-dependent NO pathway in J774.1 murine macrophages. We have confirmed previous results by demonstrating that stimulation of J774.1 with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) results in an increase in the uptake of 3H-labeled L-arginine and a concomitant increase in the production of NO. We have also shown that BCG can mimic LPS treatment, leading to enhanced L-[3H]arginine uptake by IFN-gamma-stimulated macrophages. Lipoarabinomannan, a component of the BCG cell wall that is structurally similar to LPS, is not responsible for the uptake stimulation in IFN-gamma stimulated macrophages. Although we demonstrated that there was a 2.5-fold increase in NO production by macrophages 4 h after LPS-IFN-gamma stimulation, BCG infection (with or without IFN-gamma stimulation) did not lead to the production of NO by the macrophages by 4 h postinfection. At 24 h postinfection, the infected macrophages that were stimulated with IFN-gamma produced amounts of NO similar to those of macrophages stimulated with LPS-IFN-gamma. This suggests that there are multiple regulatory pathways involved in the production of NO. Finally, our data suggest that increased expression of the arginine permease, MCAT2B, after 4 h of LPS-IFN-gamma treatment or BCG infection-IFN-gamma treatment is not sufficient to account for the increases in L-[3H]arginine uptake detected. This suggests that the activity of the L-arginine transporter(s) is also altered in response to macrophage activation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arginine homeostasis in J774.1 macrophages in the context of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(13):4830-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.01687-05. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16788192 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha blocks in vivo synthesis of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine and protection against Francisella tularensis infection in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-treated mice.Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):689-98. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.689-698.1993. Infect Immun. 1993. PMID: 8423095 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential activation of alveolar macrophages by IFN-gamma and LPS is required for enhanced growth inhibition of virulent Mycobacterium bovis but not M. bovis BCG.Immunol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;75(2):161-6. doi: 10.1038/icb.1997.22. Immunol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9107569
-
New insight into arginine and tryptophan metabolism in macrophage activation during tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1363938. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1363938. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38605962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aldehyde hypothesis: metabolic intermediates as antimicrobial effectors.Open Biol. 2022 Apr;12(4):220010. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220010. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 35414258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Tuberculosis.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 12;8:2008. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02008. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29085351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-alphabeta mediates partial control of early pulmonary Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin infection.Immunology. 2006 May;118(1):39-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02337.x. Immunology. 2006. PMID: 16630021 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acids As Mediators of Metabolic Cross Talk between Host and Pathogen.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 27;9:319. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00319. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29535717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of serum metabolic profile by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for biomarkers discovery: application in a pilot study to discriminate patients with tuberculosis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Jan 20;128(2):159-68. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.149188. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25591556 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines Impair Immunity to Helicobacter pylori by Inhibiting L-Arginine Uptake Required for Nitric Oxide Production.Gastroenterology. 2010 Nov;139(5):1686-98, 1698.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.060. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20600019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baydoun A R, Bogle R G, Pearson J D, Mann G E. Arginine uptake and metabolism in cultured murine macrophages. Agents Actions. 1993;38:C127–C129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

