Isolation and characterization of a mutant Chinese hamster ovary cell line that is resistant to Chlamydia trachomatis infection at a novel step in the attachment process
- PMID: 11500469
- PMCID: PMC98709
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5899-5904.2001
Isolation and characterization of a mutant Chinese hamster ovary cell line that is resistant to Chlamydia trachomatis infection at a novel step in the attachment process
Abstract
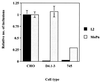
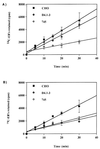
Host factors involved in Chlamydia trachomatis pathogenesis were investigated by random chemical mutagenesis of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells followed by selection for clones resistant to chlamydial infection. A clonal mutant cell line, D4.1-3, refractory to infection by the C. trachomatis L2 serovar was isolated. The D4.1-3 cell line appears to be lacking in a previously undescribed temperature-dependent and heparin-resistant binding step that occurs subsequent to engagement of cell surface heparan sulfate by L2 elementary bodies. This novel binding step differentiates the lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) serovar from other serovars and may contribute the different pathologies associated with LGV and non-LGV strains.
Figures



References
-
- Becker Y, Hochberg E, Zakay-Rones Z. Interaction of trachoma elementary bodies with host cells. Isr J Med Sci. 1969;5:121–124. - PubMed
-
- Bose S K, Paul R G. Purification of Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum elementary bodies and their interaction with HeLa cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1982;128:1371–1379. - PubMed
-
- Boutin E L, Sanderson R D, Bernfield M, Cunha G R. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in uterus and vagina alter the expression of the cell surface proteoglycan, syndecan. Dev Biol. 1991;143:63–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

