Development of a competitive index assay to evaluate the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes actA mutants during primary and secondary infection of mice
- PMID: 11500481
- PMCID: PMC98721
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5953-5957.2001
Development of a competitive index assay to evaluate the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes actA mutants during primary and secondary infection of mice
Abstract
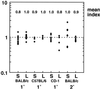
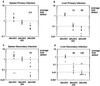
We developed a competitive index assay for murine listeriosis that tests the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes strains in different organs and at various times postinoculation. Studies presented here demonstrate the reproducibility of this assay during primary and secondary infection of inbred and outbred mice. We verified the validity of this assay by performing competitive index analysis of a well-characterized strain of L. monocytogenes lacking the actA gene. In addition, we found that while L. monocytogenes strains unable to recruit vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) to their surface exhibit a 10-fold virulence attenuation in the livers of naive animals, they display a 50-fold survival defect in the liver during secondary listeriosis.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop D K, Hinrichs D J. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes. The influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J Immunol. 1987;139:2005–2009. - PubMed
-
- Busch D H, Pilip I M, Vijh S, Pamer E G. Coordinate regulation of complex T cell populations responding to bacterial infection. Immunity. 1998;8:353–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

