A system for the generation of curves on 3D brain images
- PMID: 11500986
- PMCID: PMC6871886
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.1037
A system for the generation of curves on 3D brain images
Abstract
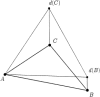
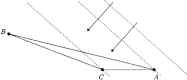
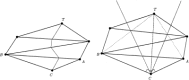
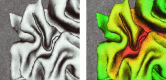
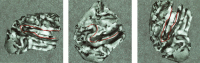
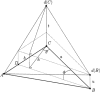
In this study, a computational optimal system for the generation of curves on triangulated surfaces representing 3D brains is described. The algorithm is based on optimally computing geodesics on the triangulated surfaces following Kimmel and Sethian ([1998]: Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:15). The system can be used to compute geodesic curves for accurate distance measurements as well as to detect sulci and gyri. These curves are defined based on local surface curvatures that are computed following a novel approach presented in this study. The corresponding software is available to the research community.
Copyright 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
 .
.













Similar articles
-
A generic framework for the parcellation of the cortical surface into gyri using geodesic Voronoï diagrams.Med Image Anal. 2003 Dec;7(4):403-16. doi: 10.1016/s1361-8415(03)00031-8. Med Image Anal. 2003. PMID: 14561546
-
Multi-manifold diffeomorphic metric mapping for aligning cortical hemispheric surfaces.Neuroimage. 2010 Jan 1;49(1):355-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.026. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 19698793
-
Mapping techniques for aligning sulci across multiple brains.Med Image Anal. 2004 Sep;8(3):295-309. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2004.06.020. Med Image Anal. 2004. PMID: 15450224 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit brain imaging.Neuroimage. 2004;23 Suppl 1:S179-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.072. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 15501087 Review.
-
Computational analysis of cerebral cortex.Neuroradiology. 2010 Aug;52(8):691-8. doi: 10.1007/s00234-010-0715-4. Epub 2010 May 18. Neuroradiology. 2010. PMID: 20480153 Review.
Cited by
-
Automatic cortical sulcal parcellation based on surface principal direction flow field tracking.Neuroimage. 2009 Jul 15;46(4):923-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.039. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19328234 Free PMC article.
-
An automated pipeline for cortical sulcal fundi extraction.Med Image Anal. 2010 Jun;14(3):343-59. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Med Image Anal. 2010. PMID: 20219410 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-automated method for delineation of landmarks on models of the cerebral cortex.J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Apr 15;178(2):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.12.025. Epub 2008 Dec 31. J Neurosci Methods. 2009. PMID: 19162074 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging discipline of Computational Functional Anatomy.Neuroimage. 2009 Mar;45(1 Suppl):S16-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.044. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19103297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of a custom-made virtual template for corrective surgeries of asymmetric patients: proof of principle and a multi-center end-user survey.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019 Mar;14(3):537-544. doi: 10.1007/s11548-018-1858-8. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019. PMID: 30250999
References
-
- Angenent S, Haker S, Tannenbaum A, Kikinis R (1998): Laplace‐Beltrami operator and brain flattening. University of Minnesota ECE Report. - PubMed
-
- Barth TJ, Sethian JA (1998): Numerical schemes for the Hamilton‐Jacobi and level set equations on triangulated domains. J Comp Physics 145: 1–40.
-
- Bertalmio M, Sapiro G, Randall G (1999): Region tracking on level‐sets methods. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18: 448–451. - PubMed
-
- Bruckstein AM (1988): On shape from shading. Comp Vision Graph Image Process 44: 139–154.
-
- Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G, Sbert C (1997): Minimal surfaces based object segmentation. IEEE‐PAMI 19: 394–398.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

