Continuous versus intermittent infusion of vancomycin in severe Staphylococcal infections: prospective multicenter randomized study
- PMID: 11502515
- PMCID: PMC90678
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.9.2460-2467.2001
Continuous versus intermittent infusion of vancomycin in severe Staphylococcal infections: prospective multicenter randomized study
Abstract
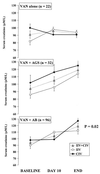
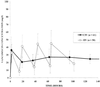
A continuous infusion of vancomycin (CIV) may provide an alternative mode of infusion in severe hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcal (MRS) infections. A multicenter, prospective, randomized study was designed to compare CIV (targeted plateau drug serum concentrations of 20 to 25 mg/liter) and intermittent infusions of vancomycin (IIV; targeted trough drug serum concentrations of 10 to 15 mg/liter) in 119 critically ill patients with MRS infections (bacteremic infections, 35%; pneumonia, 45%). Microbiological and clinical outcomes, safety, pharmacokinetics, ease of treatment adjustment, and cost were compared. Microbiological and clinical outcomes and safety were similar. CIV patients reached the targeted concentrations faster (36 +/- 31 versus 51 +/- 39 h, P = 0.029) and fewer samples were required for treatment monitoring than with IIV patients (7.7 +/- 2.2 versus 11.8 +/- 3.9 per treatment, P < 0.0001). The variability between patients in both the area under the serum concentration-time curve (AUC(24h)) and the daily dose given over 10 days of treatment was lower with CIV than with IIV (variances, 14,621 versus 53,975 mg(2)/liter(2)/h(2) [P = 0.026] and 414 versus 818 g(2) [P = 0.057], respectively). The 10-day treatment cost per patient was $454 +/- 137 in the IIV group and was 23% lower in the CIV group ($321 +/- 81: P < 0.0001). In summary, for comparable efficacy and tolerance, CIV may be a cost-effective alternative to IIV.
Figures


References
-
- Barois A, Estournet B, Moranne J B, Piliot J, Chabenat C, Bataille J. Ventricular staphylococcal infections. Treatment with vancomycin by continuous venous infusion. Presse Med. 1986;15:1805–1808. - PubMed
-
- Borderon J C, Laugier J, Chamboux C, Saliba E, Mathieu A. Continuous infusion of vancomycin during the neonatal period. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1994;42:525–529. - PubMed
-
- Brinquin L, Rousseau J M, Boulesteix G, Diraison Y, Bonsignour J R. Continuous infusion of vancomycin in post-neurosurgical staphylococcal meningitis in adults. Presse Med. 1993;22:1815–1817. - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft D W, Gault M H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Conil J M, Favarel H, Laguerre J, Brouchet A, Chabanon G, Cazal L, Bodnar M, Rouge D, Virenque C, Costagliola M. Continuous administration of vancomycin in patients with severe burns. Presse Med. 1994;23:1554–1558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

