Characterization of Sp1, AP-1, CBF and KRC binding sites and minisatellite DNA as functional elements of the metastasis-associated mts1/S100A4 gene intronic enhancer
- PMID: 11504871
- PMCID: PMC55845
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.16.3335
Characterization of Sp1, AP-1, CBF and KRC binding sites and minisatellite DNA as functional elements of the metastasis-associated mts1/S100A4 gene intronic enhancer
Abstract
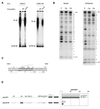
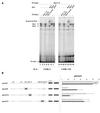
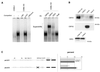
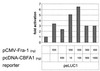
The mts1/S100A4 gene encodes a small acidic calcium-binding protein that is expressed in a cell-specific manner in development, tumorigenesis and certain tissues of adult mice. A composite enhancer that is active in murine mammary adenocarcinoma cells was previously identified in the first intron of the mts1/S100A4 gene. Here we present a detailed analysis of the structure and function of this enhancer in the Mts1/S100A4-expressing CSML100 and non-expressing CSML0 mouse adenocarcinoma cell lines. In CSML100 cells the enhancer activity is composed of at least six cis-elements interacting with Sp1 and AP-1 family members and CBF/AML/PEBP2 and KRC transcription factors. In addition, a minisatellite-like DNA sequence significantly contributes to the enhancer activity via interaction with abundant proteins, which likely have been described previously under the name minisatellite-binding proteins. Extensive mutational analysis of the mts1/S100A4 enhancer revealed a cooperative function of KRC and the factors binding minisatellite DNA. This is the first example of an enhancer where two nuclear factors earlier implicated in different recombination processes cooperate to activate transcription. In Mts1/S100A4-negative CSML0 cells the strength of the enhancer was 7- to 12.5-fold lower compared to that in CSML100 cells, when referred to the activities of three viral promoters. In CSML0 cells the enhancer could be activated by exogenous AP-1 and CBF transcription factors.
Figures




References
-
- Ebralidze A., Tulchinsky,E., Grigorian,M., Afanasjeva,A., Senin,V., Revazova,E. and Lukanidin,E. (1989) Isolation and characterization of a gene specifically expressed in different metastatic cells and whose deduced gene product has a high degree of homology to a Ca-binding protein family. Genes Dev., 3, 1086–1093. - PubMed
-
- Ambartsumian N.S., Grigorian,M.S., Larsen,I.F., Karlstrøm,O., Sidenius,N., Rygaard,J., Georgiev,G. and Lukanidin,E. (1996) Metastasis of mammary carcinomas in GRC/A hybrid mice transgenic for the mts1 gene. Oncogene, 13, 1621–1630. - PubMed
-
- Davies M.P.A., Rudland,P.S., Robertson,L., Parry,E.W., Jolicoeur,P. and Barraclough,R. (1996) Expression of the calcium-binding protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in MMTV-neu transgenic mice induces metastasis of mammary tumors. Oncogene, 13, 1631–1637. - PubMed
-
- Kriajevska M., Cardenas,M.N., Grigorian,M.S., Ambartsumjan,N.S., Georgiev,G. and Lukanidin,E. (1994) Non-muscle myosin heavy chain as a possible target for protein encoded by metastasis-related mts1 gene. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 19679–19682. - PubMed
-
- Bresnick A.R. (1999) Molecular mechanisms of nonmuscle myosin-II regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 11, 26–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

