HIF-1alpha binding to VHL is regulated by stimulus-sensitive proline hydroxylation
- PMID: 11504942
- PMCID: PMC55503
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.181341498
HIF-1alpha binding to VHL is regulated by stimulus-sensitive proline hydroxylation
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001 Dec 4;98(25):14744
Abstract
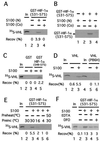
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) is a global transcriptional regulator of the hypoxic response. Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1alpha is recognized by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor protein (VHL), a component of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. This interaction thereby promotes the rapid degradation of HIF-1alpha. Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1alpha is stabilized. We have previously shown that VHL binds in a hypoxia-sensitive manner to a 27-aa segment of HIF-1alpha, and that this regulation depends on a posttranslational modification of HIF-1alpha. Through a combination of in vivo coimmunoprecipitation assays using VHL and a panel of point mutants of HIF-1alpha in this region, as well as MS and in vitro binding assays, we now provide evidence that this modification, which occurs under normoxic conditions, is hydroxylation of Pro-564 of HIF-1alpha. The data furthermore show that this proline hydroxylation is the primary regulator of VHL binding.
Figures


References
-
- Semenza G L. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell P H, Wiesener M S, Chang G W, Clifford S C, Vaux E C, Cockman M E, Wykoff C C, Pugh C W, Maher E R, Ratcliffe P J. Nature (London) 1999;399:271–275. - PubMed
-
- Cockman M E, Masson N, Mole D R, Jaakkola P, Chang G W, Clifford S C, Maher E R, Pugh C W, Ratcliffe P J, Maxwell P H. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25733–25741. - PubMed
-
- Ohh M, Park C W, Ivan M, Hoffman M A, Kim T Y, Huang L E, Pavletich N, Chau V, Kaelin W G. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:423–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

