S phase-specific proteolytic cleavage is required to activate stable DNA binding by the CDP/Cut homeodomain protein
- PMID: 11509674
- PMCID: PMC87367
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6332-6345.2001
S phase-specific proteolytic cleavage is required to activate stable DNA binding by the CDP/Cut homeodomain protein
Abstract
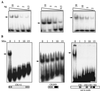
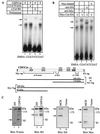
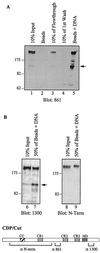
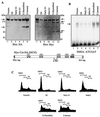
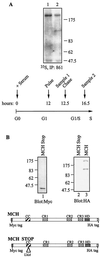
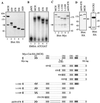
The CCAAT displacement protein (CDP), the homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster Cut protein, contains four DNA binding domains that function in pairs. Cooperation between Cut repeat 3 and the Cut homeodomain allows stable DNA binding to the ATCGAT motif, an activity previously shown to be upregulated in S phase. Here we showed that the full-length CDP/Cut protein is incapable of stable DNA binding and that the ATCGAT binding activity present in cells involves a 110-kDa carboxy-terminal peptide of CDP/Cut. A vector expressing CDP/Cut with Myc and hemagglutinin epitope tags at either end generated N- and C-terminal products of 90 and 110 kDa, suggesting that proteolytic cleavage was involved. In vivo pulse/chase labeling experiments confirmed that the 110-kDa protein was derived from the full-length CDP/Cut protein. Proteolytic processing was weak or not detectable in G(0) and G(1) but increased in populations of cells enriched in S phase, and the appearance of the 110-kDa protein coincided with the increase in ATCGAT DNA binding. Interestingly, the amino-truncated and the full-length CDP/Cut isoforms exhibited different transcriptional properties in a reporter assay. We conclude that proteolytic processing of CDP/Cut at the G(1)/S transition generates a CDP/Cut isoform with distinct DNA binding and transcriptional activities. These findings, together with the cleavage of the Scc1 protein at mitosis, suggest that site-specific proteolysis may play an important role in the regulation of cell cycle progression.
Figures



References
-
- Andres V, Chiara M D, Mahdavi V. A new bipartite DNA-binding domain: cooperative interaction between the cut repeat and homeo domain of the cut homeo proteins. Genes Dev. 1994;8:245–257. - PubMed
-
- Andres V, Nadal-Ginard B, Mahdavi V. Clox, a mammalian homeobox gene related to Drosophila cut, encodes DNA-binding regulatory proteins differentially expressed during development. Development. 1992;116:321–334. - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Ramirez-Weber F A, Laget M P, Schwartz C, Kornberg T B. Proteolysis that is inhibited by hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell. 1997;89:1043–1053. - PubMed
-
- Aziz F, Vanwijnen A J, Vanghan P S, Wu S J, Shakoori A R, Lian J B, Soprano K J, Stein J L, Stein G S. The integrated activities of Irf-2 (Hinf-M), Cdp/Cut (Hinf-D) and H4tf-2 (Hinf-P) regulate transcription of a cell cycle controlled human histone H4 gene - mechanistic differences between distinct H4 genes. Mol Biol Rep. 1998;25:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
