Sequential actions of BMP receptors control neural precursor cell production and fate
- PMID: 11511541
- PMCID: PMC312756
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.894701
Sequential actions of BMP receptors control neural precursor cell production and fate
Abstract
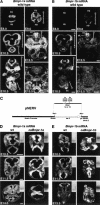
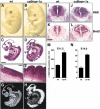
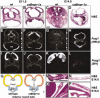
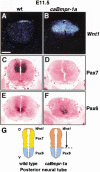
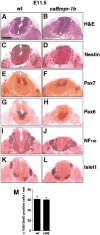
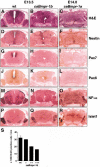
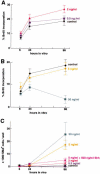
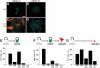
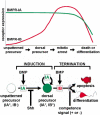
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) have diverse and sometimes paradoxical effects during embryonic development. To determine the mechanisms underlying BMP actions, we analyzed the expression and function of two BMP receptors, BMPR-IA and BMPR-IB, in neural precursor cells in vitro and in vivo. Neural precursor cells always express Bmpr-1a, but Bmpr-1b is not expressed until embryonic day 9 and is restricted to the dorsal neural tube surrounding the source of BMP ligands. BMPR-IA activation induces (and Sonic hedgehog prevents) expression of Bmpr-1b along with dorsal identity genes in precursor cells and promotes their proliferation. When BMPR-IB is activated, it limits precursor cell numbers by causing mitotic arrest. This results in apoptosis in early gestation embryos and terminal differentiation in mid-gestation embryos. Thus, BMP actions are first inducing (through BMPR-IA) and then terminating (through BMPR-IB), based on the accumulation of BMPR-IB relative to BMPR-IA. We describe a feed-forward mechanism to explain how the sequential actions of these receptors control the production and fate of dorsal precursor cells from neural stem cells.
Figures


References
-
- Altmann CR, Brivanlou AH. Neural patterning in the vertebrate embryo. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;203:447–482. - PubMed
-
- Amthor H, Christ B, Weil M, Patel K. The importance of timing differentiation during limb muscle development. Curr Biol. 1998;8:642–652. - PubMed
-
- Amthor H, Christ B, Patel K. A molecular mechanism enabling continuous embryonic muscle growth: A balance between proliferation and differentiation. Development. 1999;126:1041–1053. - PubMed
-
- Arkell R, Beddington RS. BMP-7 influences pattern and growth of the developing hindbrain of mouse embryos. Development. 1997;124:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Kemp C, Belo JA, Anderson RM, May SR, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Harland RM, Rossant J, et al. The organizer factors Chordin and Noggin are required for mouse forebrain development. Nature. 2000;403:658–661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
