Regulated secretion of YopN by the type III machinery of Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 11514512
- PMCID: PMC95411
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.18.5293-5301.2001
Regulated secretion of YopN by the type III machinery of Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
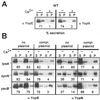
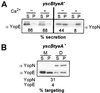
During infection, Yersinia enterocolitica exports Yop proteins via a type III secretion pathway. Secretion is activated when the environmental concentration of calcium ions is below 100 microM (low-calcium response). Yersiniae lacking yopN (lcrE), yscB, sycN, or tyeA do not inactivate the type III pathway even when the concentration of calcium is above 100 microM (calcium-blind phenotype). Purified YscB and SycN proteins form cytoplasmic complexes that bind a region including amino acids 16 to 100 of YopN, whereas TyeA binds YopN residues 101 to 294. Translational fusion of yopN gene sequences to the 5' end of the npt reporter generates hybrid proteins that are transported by the type III pathway. The signal necessary and sufficient for the type III secretion of hybrid proteins is located within the first 15 codons of yopN. Expression of plasmid-borne yopN, but not of yopN(1-294)-npt, complements the calcium-blind phenotype of yopN mutants. Surprisingly, yopN mutants respond to environmental changes in calcium concentration and secrete YopN(1-294)-Npt in the absence but not in the presence of calcium. tyeA is required for the low-calcium regulation of YopN(1-294)-Npt secretion, whereas sycN and yscB mutants fail to secrete YopN(1-294)-Npt in the presence of calcium. Experiments with yopN-npt fusions identified two other signals that regulate the secretion of YopN. yopN codons 16 to 100 prevent the entry of YopN into the type III pathway, a negative regulatory effect that is overcome by expression of yscB and sycN. The portion of YopN encoded by codons 101 to 294 prevents transport of the polypeptide across the bacterial double membrane envelope in the presence of functional tyeA. These data support a model whereby YopN transport may serve as a regulatory mechanism for the activity of the type III pathway. YscB/SycN binding facilitates the initiation of YopN into the type III pathway, whereas TyeA binding prevents transport of the polypeptide across the bacterial envelope. Changes in the environmental calcium concentration relieve the TyeA-mediated regulation, triggering YopN transport and activating the type III pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The SycN/YscB chaperone-binding domain of YopN is required for the calcium-dependent regulation of Yop secretion by Yersinia pestis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Jan 24;3:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00001. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23355975 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and characterization of Yersinia pestis YopN mutants that constitutively block Yop secretion.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(4):970-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04738.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16091038
-
A complex composed of SycN and YscB functions as a specific chaperone for YopN in Yersinia pestis.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Nov;30(4):777-88. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01110.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 10094626
-
The Yersinia pestis type III secretion system: expression, assembly and role in the evasion of host defenses.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):237-45. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8454-3. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24198067 Review.
-
The virulence plasmid of Yersinia, an antihost genome.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998 Dec;62(4):1315-52. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.62.4.1315-1352.1998. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9841674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
YopN and TyeA Hydrophobic Contacts Required for Regulating Ysc-Yop Type III Secretion Activity by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Jun 21;6:66. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00066. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27446813 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella Type III Secretion Injectosome and Effector Proteins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 4;10:466. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00466. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33014891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type Three Secretion System in Attaching and Effacing Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Oct 21;6:129. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00129. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27818950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YopK controls both rate and fidelity of Yop translocation.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jan;87(2):301-17. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12099. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23205707 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of chromosomal genes in Yersinia pestis that influence type III secretion and delivery of Yops into target cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034039. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allaoui A, Schulte R, Cornelis G R. Mutational analysis of the Yersinia enterocolitica virC operon: characterization of yscE, F, G, I, J, K required for Yop secretion and yscH encoding YopR. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:343–355. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D M, Schneewind O. A mRNA signal for the type III secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. Science. 1997;278:1140–1143. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D M, Schneewind O. Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion: an mRNA signal that couples translation and secretion of YopQ. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31:1139–1148. - PubMed
-
- Barrero M J, Montero M, Alvarez J. Dynamics of [Ca2+] in the endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm of intact HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27694–27699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

