Microaerophilic induction of the alpha-crystallin chaperone protein homologue (hspX) mRNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 11514514
- PMCID: PMC95413
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.18.5311-5316.2001
Microaerophilic induction of the alpha-crystallin chaperone protein homologue (hspX) mRNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
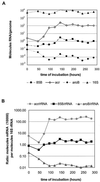
Among the products that are expressed when Mycobacterium tuberculosis undergoes hypoxic shiftdown to nonreplicating persistence (NRP) is the alpha-crystallin chaperone protein homologue (Acr). This expression coincides with the previously reported appearance of a respiratory type of nitrate reductase activity, the increase in glycine dehydrogenase activity, and the production of a unique antigen, URB-1. In a timed sampling study, using a slowly stirred oxygen depletion culture model, we have demonstrated that the hspX mRNA that codes for Acr protein as well as the protein itself is induced just as the bacilli enter the microaerophilic NRP stage 1 (NRP-1). In contrast to the induction observed for hspX mRNA, levels of 16S rRNA, fbpB mRNA (encoding the 85B alpha antigen), and aroB mRNA (encoding dehydroquinate synthase) demonstrate relatively small to no change upon entering NRP-1. Acr protein was shown to be identical to URB-1 by Western analysis with anti-URB-1 antibody. The fact that antibody to Acr is found in a high percentage of tuberculosis patients suggests that the hypoxic shiftdown of tubercle bacilli to the NRP state that occurs in vitro, resulting in production of the alpha-crystallin protein, occurs in vivo as well. Simultaneous abrupt increases in hspX mRNA and Acr protein suggest that Acr protein expression is controlled at the level of transcription.
Figures


References
-
- Belisle J T, Vissa V D, Sievert T, Takayama K, Brennan P J, Besra G S. Role of the major antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in cell wall biogenesis. Science. 1997;276:1420–1422. - PubMed
-
- Cole S T, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon S V, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry III C E, Tekaia F, Badcock K, Basham O, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Connor R, Davies R, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Hamlin N, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Jagels K, Krogh A, McLean J, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Osborne J, Quail M A, Rajandream M-A, Rogers J, Rutter S, Seeger K, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston J E, Taylor T, Whitehead S, Barrell B G. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature. 1998;393:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Desjardin, L. E. Isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA from sputum. In S. H. Gillespie (ed.), Antibiotic resistance methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J., in press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

