Cohesin-dockerin interactions of cellulosomal subunits of Clostridium cellulovorans
- PMID: 11514529
- PMCID: PMC95428
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.18.5431-5435.2001
Cohesin-dockerin interactions of cellulosomal subunits of Clostridium cellulovorans
Abstract
The cellulosome of Clostridium cellulovorans consists of three major subunits: CbpA, EngE, and ExgS. The C. cellulovorans scaffolding protein (CbpA) contains nine hydrophobic repeated domains (cohesins) for the binding of enzymatic subunits. Cohesin domains are quite homologous, but there are some questions regarding their binding specificity because some of the domains have regions of low-level sequence similarity. Two cohesins which exhibit 60% sequence similarity were investigated for their ability to bind cellulosomal enzymes. Cohesin 1 (Coh1) was found to contain amino acid residues corresponding to amino acids 312 to 453 of CbpA, which contains a total of 1,848 amino acid residues. Coh6 was determined to contain amino acid residues corresponding to residues 1113 to 1254 of CbpA. By genetic construction, these two cohesins were each fused to MalE, producing MalE-Coh1 and MalE-Coh6. The abilities of two fusion proteins to bind to EngE, ExgS, and CbpA were compared. Although MalE-Coh6 could bind EngE and ExgS, little or no binding of the enzymatic subunits was observed with MalE-Coh1. Significantly, the abilities of the two fusion proteins to bind CbpA were similar. The binding of dockerin-containing enzymes to cohesin-containing proteins was suggested as a model for assembly of cellulosomes. In our examination of the role of dockerins, it was also shown that the binding of endoglucanase B (EngB) to CbpA was dependent on the presence of EngB's dockerin. These results suggest that different cohesins may function with differing efficiency and specificity, that cohesins may play some role in the formation of polycellulosomes through Coh-CbpA interactions, and that dockerins play an important role during the interaction of cellulosomal enzymes and cohesins present in CbpA.
Figures


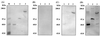

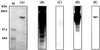
Similar articles
-
Degradation of corn fiber by Clostridium cellulovorans cellulases and hemicellulases and contribution of scaffolding protein CbpA.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;71(7):3504-11. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.3504-3511.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16000754 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of multiple copies of cohesins on cellulase and hemicellulase activities of Clostridium cellulovorans mini-cellulosomes.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Nov;17(11):1782-8. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18092461
-
The Clostridium cellulovorans cellulosome: an enzyme complex with plant cell wall degrading activity.Chem Rec. 2001;1(1):24-32. doi: 10.1002/1528-0691(2001)1:1<24::AID-TCR5>3.0.CO;2-W. Chem Rec. 2001. PMID: 11893054 Review.
-
Synergistic effects on crystalline cellulose degradation between cellulosomal cellulases from Clostridium cellulovorans.J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5088-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.18.5088-5095.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12193625 Free PMC article.
-
The Clostridium cellulovorans cellulosome.Crit Rev Microbiol. 1994;20(2):87-93. doi: 10.3109/10408419409113548. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8080629 Review.
Cited by
-
A rhamnogalacturonan lyase in the Clostridium cellulolyticum cellulosome.J Bacteriol. 2003 Aug;185(16):4727-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.16.4727-4733.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12896991 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate-Related Factors Affecting Cellulosome-Induced Hydrolysis for Lignocellulose Valorization.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 8;20(13):3354. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133354. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel organization and divergent dockerin specificities in the cellulosome system of Ruminococcus flavefaciens.J Bacteriol. 2003 Feb;185(3):703-13. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.3.703-713.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12533446 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and expression of the xynB gene and its product, XynB, a consistent component of the Clostridium cellulovorans cellulosome.J Bacteriol. 2004 Dec;186(24):8347-55. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.24.8347-8355.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15576784 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulase, clostridia, and ethanol.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Mar;69(1):124-54. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.1.124-154.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15755956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doi R H, Tamaru Y. The Clostridium cellulovorans cellulosome: an enzyme complex with plant cell wall degrading activity. Chem Rec. 2001;1:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Fierobe H-P, Pagès S, Belaich A, Champ S, Lexa D, Belaich J-P. Cellulosome from Clostridium cellulolyticum: molecular study of the dockerin/cohesin interaction. Biochemistry. 1999;38:12822–12832. - PubMed
-
- Foong F, Hamamoto T, Shoseyov O, Doi R H. Nucleotide sequence and characteristics of endoglucanase gene engB from Clostridium cellulovorans. J Gen Microbiol. 1991;137:1729–1736. - PubMed
-
- Gerngross U, Romaniec M P M, Kobayashi T, Huskisson N S, Demain A L. Sequencing of a Clostridium thermocellum gene (cipA) encoding the cellulosomal SL-protein reveals an unusual degree of internal homology. Mol Microbiol. 1993;8:325–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

