Yellow fever vector live-virus vaccines: West Nile virus vaccine development
- PMID: 11516995
- PMCID: PMC7140174
- DOI: 10.1016/s1471-4914(01)02048-2
Yellow fever vector live-virus vaccines: West Nile virus vaccine development
Abstract
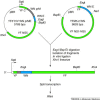
By combining molecular-biological techniques with our increased understanding of the effect of gene sequence modification on viral function, yellow fever 17D, a positive-strand RNA virus vaccine, has been manipulated to induce a protective immune response against viruses of the same family (e.g. Japanese encephalitis and dengue viruses). Triggered by the emergence of West Nile virus infections in the New World afflicting humans, horses and birds, the success of this recombinant technology has prompted the rapid development of a live-virus attenuated candidate vaccine against West Nile virus.
Figures

References
-
- Carter H., Campbell H. Rational use of measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Drugs. 1993;45:677–683. - PubMed
-
- Kawashima H. Detection and sequencing of measles virus from peripheral mononuclear cells from patients with inflammatory bowel disease and autism. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000;45:723–729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

