Serotonin receptors modulate GABA(A) receptor channels through activation of anchored protein kinase C in prefrontal cortical neurons
- PMID: 11517239
- PMCID: PMC6763081
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-17-06502.2001
Serotonin receptors modulate GABA(A) receptor channels through activation of anchored protein kinase C in prefrontal cortical neurons
Abstract
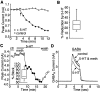
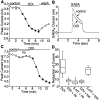
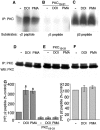
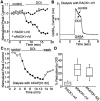
Serotonergic neurotransmission in prefrontal cortex (PFC) has long been known to play a key role in regulating emotion and cognition under normal and pathological conditions. However, the cellular mechanisms by which this regulation occurs are unclear. In this study, we examined the impact of serotonin on GABA(A) receptor channels in PFC pyramidal neurons using combined patch-clamp recording, biochemical, and molecular approaches. Application of serotonin produced a reduction of postsynaptic GABA(A) receptor currents. Although multiple 5-HT receptors were coexpressed in PFC pyramidal neurons, the serotonergic modulation of GABA-evoked currents was mimicked by the 5-HT(2)-class agonist (-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine and blocked by 5-HT(2) antagonists risperidone and ketanserin, indicating the mediation by 5-HT(2) receptors. Inhibiting phospholipase C blocked the 5-HT(2) inhibition of GABA(A) currents, as did dialysis with protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitory peptide. Moreover, activation of 5-HT(2) receptors in PFC slices increased the in vitro kinase activity of PKC toward GABA(A) receptor gamma2 subunits. Disrupting the interaction of PKC with its anchoring protein RACK1 (receptor for activated C kinase) eliminated the 5-HT(2) modulation of GABA(A) currents, suggesting that RACK1-mediated targeting of PKC to the vicinity of GABA(A) receptors is required for the serotonergic signaling. Together, our results show that activation of 5-HT(2) receptors in PFC pyramidal neurons inhibits GABA(A) currents through phosphorylation of GABA(A) receptors by the activation of anchored PKC. The suppression of GABAergic signaling provides a novel mechanism for serotonergic modulation of PFC neuronal activity, which may underlie the actions of many antidepressant drugs.
Figures



References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M, Aghajanian GK, Charney D, Krystal J. The role of serotonin in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997;9:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Andrade R. Regulation of membrane excitability in the central nervous system by serotonin receptor subtypes. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1998;861:190–203. - PubMed
-
- Araneda R, Andrade RA. 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A receptors mediate opposing responses on membrane excitability in rat association cortex. Neuroscience. 1991;40:399–412. - PubMed
-
- Battaini F, Pascale A, Paoletti R, Govoni S. The role of anchoring protein RACK1 in PKC activation in the aging rat brain. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:410–415. - PubMed
-
- Baxter G, Kennett G, Blaney F, Blackburn T. 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family re-united? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995;16:105–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
