Modeling circadian oscillations with interlocking positive and negative feedback loops
- PMID: 11517254
- PMCID: PMC6763090
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-17-06644.2001
Modeling circadian oscillations with interlocking positive and negative feedback loops
Abstract
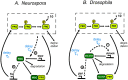
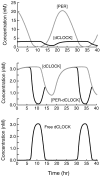
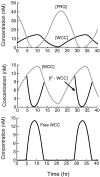
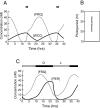
Both positive and negative feedback loops of transcriptional regulation have been proposed to be important for the generation of circadian rhythms. To test the sufficiency of the proposed mechanisms, two differential equation-based models were constructed to describe the Neurospora crassa and Drosophila melanogaster circadian oscillators. In the model of the Neurospora oscillator, FRQ suppresses frq transcription by binding to a complex of the transcriptional activators WC-1 and WC-2, thus yielding negative feedback. FRQ also activates synthesis of WC-1, which in turn activates frq transcription, yielding positive feedback. In the model of the Drosophila oscillator, PER and TIM are represented by a "lumped" variable, "PER." PER suppresses its own transcription by binding to the transcriptional regulator dCLOCK, thus yielding negative feedback. PER also binds to dCLOCK to de-repress dclock, and dCLOCK in turn activates per transcription, yielding positive feedback. Both models displayed circadian oscillations that were robust to parameter variations and to noise and that entrained to simulated light/dark cycles. Circadian oscillations were only obtained if time delays were included to represent processes not modeled in detail (e.g., transcription and translation). In both models, oscillations were preserved when positive feedback was removed.
Figures

References
-
- Barkai N, Leibler S. Circadian clocks limited by noise. Nature. 2000;403:267–268. - PubMed
-
- Crosthwaite SK, Dunlap JC, Loros JJ. Light-induced resetting of a circadian clock is mediated by a rapid increase in frequency transcript. Cell. 1995;81:1003–1012. - PubMed
-
- Crosthwaite SK, Dunlap JC, Loros JJ. Neurospora wc-1 and wc-2: transcription, photoresponses, and the origins of circadian rhythmicity. Science. 1997;276:763–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
