A conformational change in the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center upon active/inactive transition
- PMID: 11517305
- PMCID: PMC56921
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.171319598
A conformational change in the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center upon active/inactive transition
Abstract
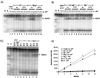
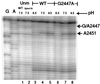
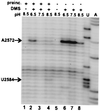
The ribosome is a dynamic particle that undergoes many structural changes during translation. We show through chemical probing with dimethyl sulfate (DMS) that conformational changes occur at several nucleotides in the peptidyl transferase center upon alterations in pH, temperature, and monovalent ion concentration, consistent with observations made by Elson and coworkers over 30 years ago. Moreover, we have found that the pH-dependent DMS reactivity of A2451 in the center of the 23S rRNA peptidyl transferase region, ascribed to a perturbed pKa of this base, occurs only in inactive 50S and 70S ribosomes. The degree of DMS reactivity of this base in the inactive ribosomes depends on both the identity and amount of monovalent ion present. Furthermore, G2447, a residue proposed to be critical for the hypothesized pKa perturbation, is not essential for the conditional DMS reactivity at A2451. Given that the pH-dependent change in DMS reactivity at A2451 occurs only in inactive ribosomes, and that this DMS reactivity can increase with increasing salt (independently of pH), we conclude that this observation cannot be used as supporting evidence for a recently proposed model of acid/base catalyzed ribosomal transpeptidation.
Figures

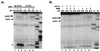
References
-
- Frank J, Agrawal R K. Nature (London) 2000;406:318–322. - PubMed
-
- Ogle J M, Brodersen D E, Clemons W M, Jr, Tarry M J, Carter A P, Ramakrishnan V. Science. 2001;292:897–902. - PubMed
-
- Stark H, Rodnina M V, Wieden H-J, van Heel M, Wintermeyer W. Cell. 2000;100:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Yusopov M M, Yusopova G Z, Baucom A, Lieberman K, Earnest T N, Cate J H D, Noller H F. Science. 2001;292:883–896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

