Critical role for the chemokine MCP-1/CCR2 in the pathogenesis of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome
- PMID: 11518728
- PMCID: PMC209398
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12214
Critical role for the chemokine MCP-1/CCR2 in the pathogenesis of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome
Abstract
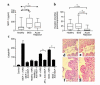
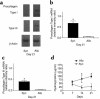
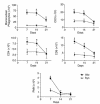
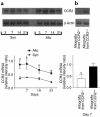
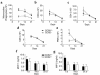
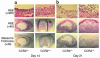
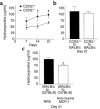
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is the major limitation to survival after lung transplantation. Acute rejection, its main risk factor, is characterized by perivascular/bronchiolar leukocyte infiltration. BOS is characterized by persistent peribronchiolar leukocyte recruitment leading to airway fibrosis and obliteration. The specific mechanism(s) by which these leukocytes are recruited are unknown. Because MCP-1, acting through its receptor CCR2, is a potent mononuclear cell chemoattractant, we hypothesized that expression of this chemokine during an allogeneic-response promotes persistent recruitment of leukocytes and, ultimately, rejection. We found that elevated levels of biologically active MCP-1 in human bronchial lavage fluid (BALF) were associated with the continuum from acute to chronic allograft rejection. Translational studies in a murine model of BOS demonstrated increased MCP-1 expression paralleling mononuclear cell recruitment and CCR2 expression. Loss of MCP-1/CCR2 signaling, as seen in CCR2(-/-) mice or in WT mice treated with neutralizing antibodies to MCP-1, significantly reduced recruitment of mononuclear phagocytes following tracheal transplantation and led to attenuation of BOS. Lymphocyte infiltration was not reduced under these conditions. We suggest that MCP-1/CCR2 signaling plays an important role in recruitment of mononuclear phagocytes, a pivotal event in the pathogenesis of BOS.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

