Impact of the six nucleotides downstream of the stop codon on translation termination
- PMID: 11520858
- PMCID: PMC1084031
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve176
Impact of the six nucleotides downstream of the stop codon on translation termination
Abstract
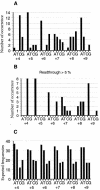
The efficiency of translation termination is influenced by local contexts surrounding stop codons. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, upstream and downstream sequences act synergistically to influence the translation termination efficiency. By analysing derivatives of a leaky stop codon context, we initially demonstrated that at least six nucleotides after the stop codon are a key determinant of readthrough efficiency in S. cerevisiae. We then developed a combinatorial-based strategy to identify poor 3' termination contexts. By screening a degenerate oligonucleotide library, we identified a consensus sequence -CA(A/G)N(U/C/G)A-, which promotes >5% readthrough efficiency when located downstream of a UAG stop codon. Potential base pairing between this stimulatory motif and regions close to helix 18 and 44 of the 18S rRNA provides a model for the effect of the 3' stop codon context on translation termination.
Figures

References
-
- Arkov A.L., Freistroffer, D.V., Pavlov, M.Y., Ehrenberg, M. and Murgola, E.J. (2000) Mutations in conserved regions of ribosomal RNAs decrease the productive association of peptide-chain release factors with the ribosome during translation termination. Biochimie, 82, 671–682. - PubMed
-
- Bonetti B., Fu, L.W., Moon, J. and Bedwell, D.M. (1995) The efficiency of translation termination is determined by a synergistic interplay between upstream and downstream sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol., 251, 334–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

