Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function
- PMID: 11520916
- PMCID: PMC2758233
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.677
Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function
Abstract
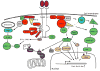
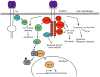
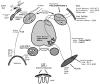
Neurotrophins regulate development, maintenance, and function of vertebrate nervous systems. Neurotrophins activate two different classes of receptors, the Trk family of receptor tyrosine kinases and p75NTR, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. Through these, neurotrophins activate many signaling pathways, including those mediated by ras and members of the cdc-42/ras/rho G protein families, and the MAP kinase, PI-3 kinase, and Jun kinase cascades. During development, limiting amounts of neurotrophins function as survival factors to ensure a match between the number of surviving neurons and the requirement for appropriate target innervation. They also regulate cell fate decisions, axon growth, dendrite pruning, the patterning of innervation and the expression of proteins crucial for normal neuronal function, such as neurotransmitters and ion channels. These proteins also regulate many aspects of neural function. In the mature nervous system, they control synaptic function and synaptic plasticity, while continuing to modulate neuronal survival.
Figures
References
-
- Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP, DeChiara TM, Russell M, et al. A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death. Nature. 1995;374:450–53. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Stark GR. The p53 network. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Koltzenburg M, Lewin GR, Masu Y, Helbig C, et al. Specific subtypes of cutaneous mechanoreceptors require neurotrophin-3 following peripheral target innervation. Neuron. 1996;16:287–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

