VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell PAF synthesis is mediated by group V 14 kDa secretory phospholipase A2
- PMID: 11522612
- PMCID: PMC1572915
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704215
VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell PAF synthesis is mediated by group V 14 kDa secretory phospholipase A2
Abstract
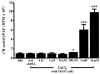
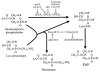
1. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent inducer of inflammation, and we have shown that this latter effect is mediated through endothelial cell (EC) PAF synthesis. Since the phospholipid remodelling pathway enzymes (CoA-independent transacylase, CoA-IT; phospholipase A2, PLA2; and lyso-PAF acetyltransferase, lyso-PAF-AT) may participate in PAF synthesis, we assessed their contribution to VEGF-induced PAF synthesis in bovine aortic EC (BAEC) and human umbilical vein EC (HUVEC). 2. VEGF enhanced BAEC and HUVEC PAF synthesis by up to 28 and 4 fold above basal levels respectively. 3. A pretreatment with a CoA-IT and lyso-PAF-AT inhibitor (Sanguinarin; 500 nM) blocked VEGF-induced PAF synthesis by 95%, a specific CoA-IT inhibitor (SKF45905; 10 - 50 microM) was without effect, confirming the crucial role of the PLA2 and lyso-PAF-AT. 4. Treatment with secreted PLA2 (sPLA2) inhibitors which have been shown to inhibit both groups IIA and V sPLA2 (SB203347; 10 microM and LY311727; 100 microM) blocked EC PAF synthesis by up to 90%, whereas selective inhibition of group IIA sPLA2 (LY311727; 1 microM) had no significant effect. 5. RT - PCR and Western blot analyses demonstrated the presence of group V sPLA2 whereas group IIA sPLA2 was undetected in EC. 6. Treatment with cytosolic and calcium-independent PLA2 inhibitors (Arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone, Bromoenol lactone, Methyl arachydonyl fluorophosphate, up to 50 microM) did not prevent but rather potentiated the VEGF effect on EC PAF synthesis. 7. These results provide evidence that with VEGF activation of EC cells, the group V sPLA2 provides substrate for EC PAF formation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immediate and delayed VEGF-mediated NO synthesis in endothelial cells: role of PI3K, PKC and PLC pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Dec;137(7):1021-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704956. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12429574 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of VEGF-induced endothelial cell PAF synthesis: role of p42/44 MAPK, p38 MAPK and PI3K pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Nov;134(6):1253-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704367. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11704645 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that 85 kDa phospholipase A2 is not linked to CoA-independent transacylase-mediated production of platelet-activating factor in human monocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Jun 2;1346(2):173-84. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(97)00032-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997. PMID: 9219900
-
Distinguishing phospholipase A2 types in biological samples by employing group-specific assays in the presence of inhibitors.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005 Sep;77(1-4):235-48. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2005.02.004. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005. PMID: 16099408 Review.
-
Secretory phospholipase A2 of group IIA: is it an offensive or a defensive player during atherosclerosis and other inflammatory diseases?Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2006 Mar;79(1-2):1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2005.10.005. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2006. PMID: 16516807 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro anti-Plasmodium falciparum properties of the full set of human secreted phospholipases A2.Infect Immun. 2015 Jun;83(6):2453-65. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02474-14. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25824843 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical induction of group V phospholipase A(2) causes lung inflammation and acute lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 May 15;304(10):L689-700. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00047.2013. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23525785 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and quantification of microparticles from different cellular lineages using flow cytometry. Evaluation of the impact of secreted phospholipase A2 on microparticle assessment.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 14;10(1):e0116812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116812. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25587983 Free PMC article.
-
Prohibitin-1 maintains the angiogenic capacity of endothelial cells by regulating mitochondrial function and senescence.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jan 14;180(1):101-12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200706072. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18195103 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate and delayed VEGF-mediated NO synthesis in endothelial cells: role of PI3K, PKC and PLC pathways.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Dec;137(7):1021-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704956. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12429574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACKERMANN E.J., CONDE-FRIEBOES K., DENNIS E.A. Inhibition of macrophage Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:445–450. - PubMed
-
- BALBOA M.A., BALSINDE J., WINSTEAD M.V., TISHFIELD J.A., DENNIS E.A. Novel group V phospholipase A2 involved in arachidonic acid mobilization in murine P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:32381–32384. - PubMed
-
- BALSINDE J.J, , BALBOA M.A., DENNIS E.A. Antisense inhibition of Group VI Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 blocks phospholipid fatty acid remodeling in murine P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:29317–29321. - PubMed
-
- BALSINDE J., DENNIS E.A. Bromoenol lactone inhibits magnesium-dependent phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and blocks triacylglycerol biosynthesis in mouse P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:31937–31941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

