Transcription activation by targeted recruitment of the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1
- PMID: 11522823
- PMCID: PMC55871
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.17.3539
Transcription activation by targeted recruitment of the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1
Erratum in
-
Editor's Note to 'Transcription activation by targeted recruitment of the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 12;50(14):8399. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac622. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35848923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
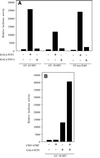
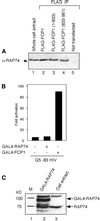
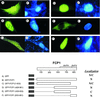
Human FCP1 in association with RNAP II reconstitutes a highly specific CTD phosphatase activity and is required for recycling RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) in vitro. Here we demonstrate that targeted recruitment of FCP1 to promoter templates, through fusion to a DNA-binding domain, stimulates transcription. We demonstrate that a short region at the C-terminus of the FCP1 protein is required and sufficient for activation, indicating that neither the N-terminal phosphatase domain nor the BRCT domains are required for transcription activity of DNA-bound FCP1. In addition, we demonstrate that the C-terminus region of FCP1 suffices for efficient binding in vivo to the RAP74 subunit of TFIIF and is also required for the exclusive nuclear localization of the protein. These findings suggest a role for FCP1 as a positive regulator of RNAP II transcription.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editor's Note to 'Transcription activation by targeted recruitment of the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 12;50(14):8399. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac622. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35848923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Enhanced binding of RNAP II CTD phosphatase FCP1 to RAP74 following CK2 phosphorylation.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 1;44(8):2732-45. doi: 10.1021/bi047958h. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15723518
-
Interactions of the HIV-1 Tat and RAP74 proteins with the RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase FCP1.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 1;44(8):2716-31. doi: 10.1021/bi047957p. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15723517
-
A motif shared by TFIIF and TFIIB mediates their interaction with the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain phosphatase Fcp1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;20(20):7438-49. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.20.7438-7449.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11003641 Free PMC article.
-
CTD phosphatase: role in RNA polymerase II cycling and the regulation of transcript elongation.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2002;72:333-65. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(02)72074-6. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12206456 Review.
-
The RNA Polymerase II CTD: The Increasing Complexity of a Low-Complexity Protein Domain.J Mol Biol. 2016 Jun 19;428(12):2607-2622. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.006. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26876604 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Protein Phosphatase Expressions on the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 20;9(9):10299-10331. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07787. eCollection 2024 Mar 5. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38463290 Free PMC article.
-
CDK9/cyclin complexes modulate endoderm induction by direct interaction with Mix.3/mixer.Dev Dyn. 2009 Jun;238(6):1346-57. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21920. Dev Dyn. 2009. PMID: 19347956 Free PMC article.
-
NMR structure of a complex containing the TFIIF subunit RAP74 and the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain phosphatase FCP1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 13;100(10):5688-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1031524100. Epub 2003 May 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12732728 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal domain phosphatase and transcription elongation activities of FCP1 are regulated by phosphorylation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 4;100(5):2328-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2628049100. Epub 2003 Feb 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12591939 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of CTDP1 inhibits lung cancer cell growth in vitro.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Apr;142(4):723-32. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2070-7. Epub 2015 Nov 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26590573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dahmus M.E. (1996) Reversible phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 19009–19012. - PubMed
-
- Zawel L., Lu,H., Cisek,L.J., Corden,J.L. and Reinberg,D. (1993) The cycling of RNA polymerase II during transcription. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 58, 187–198. - PubMed
-
- Dahmus M.E. (1994) The role of multisite phosphorylation in the regulation of RNA polymerase II activity. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 48, 143–179. - PubMed
-
- Conaway J., Shilatifard,A., Dvir,A. and Conaway,R.C. (2000) Control of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Trends Cell Biol., 25, 375–380. - PubMed

