Association of galectin-1 and galectin-3 with Gemin4 in complexes containing the SMN protein
- PMID: 11522829
- PMCID: PMC55878
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.17.3595
Association of galectin-1 and galectin-3 with Gemin4 in complexes containing the SMN protein
Abstract
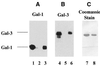
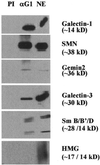
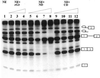
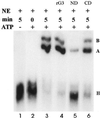
In previous studies we showed that galectin-1 and galectin-3 are factors required for the splicing of pre-mRNA, as assayed in a cell-free system. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen with galectin-1 as bait, Gemin4 was identified as a putative interacting protein. Gemin4 is one component of a macromolecular complex containing approximately 15 polypeptides, including SMN (survival of motor neuron) protein. Rabbit anti-galectin-1 co-immunoprecipitated from HeLa cell nuclear extracts, along with galectin-1, polypeptides identified to be in this complex: SMN, Gemin2 and the Sm polypeptides of snRNPs. Direct interaction between Gemin4 and galectin-1 was demonstrated in glutathione S-transferase (GST) pull-down assays. We also found that galectin-3 interacted with Gemin4 and that it constituted one component of the complex co-immunoprecipitated with galectin-1. Indeed, fragments of either Gemin4 or galectin-3 exhibited a dominant negative effect when added to a cell-free splicing assay. For example, a dose-dependent inhibition of splicing was observed in the presence of exogenously added N-terminal domain of galectin-3 polypeptide. In contrast, parallel addition of either the intact galectin-3 polypeptide or the C-terminal domain failed to yield the same effect. Using native gel electrophoresis to detect complexes formed by the splicing extract, we found that with addition of the N-terminal domain the predominant portion of the radiolabeled pre-mRNA was arrested at a position corresponding to the H-complex. Inasmuch as SMN-containing complexes have been implicated in the delivery of snRNPs to the H-complex, these results provide strong evidence that galectin-1 and galectin-3, by interacting with Gemin4, play a role in spliceosome assembly in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of a nuclear 20S complex containing the survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein and a specific subset of spliceosomal Sm proteins.Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Aug 12;9(13):1977-86. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.13.1977. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. PMID: 10942426
-
Gemin4. A novel component of the SMN complex that is found in both gems and nucleoli.J Cell Biol. 2000 Mar 20;148(6):1177-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.6.1177. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10725331 Free PMC article.
-
Gemin5, a novel WD repeat protein component of the SMN complex that binds Sm proteins.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 15;277(7):5631-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109448200. Epub 2001 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11714716
-
Understanding the biochemical activities of galectin-1 and galectin-3 in the nucleus.Glycoconj J. 2002;19(7-9):499-506. doi: 10.1023/B:GLYC.0000014079.87862.c7. Glycoconj J. 2002. PMID: 14758073 Review.
-
[Advance in researches on survival of motor neurons protein and its interaction proteins].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Oct;20(5):430-2. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14556199 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Possible Effects of Galectin-3 on Mechanisms of Renal and Hepatocellular Injury Induced by Intravascular Hemolysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8129. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158129. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3, Possible Role in Pathogenesis of Periodontal Diseases and Potential Therapeutic Target.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 19;12:638258. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.638258. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33815121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of galectin-3 changes the gene expression and augments the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents.Cancer Sci. 2010 Jan;101(1):94-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01364.x. Epub 2009 Sep 14. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 19843071 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear presence of adhesion-/growth-regulatory galectins in normal/malignant cells of squamous epithelial origin.Histochem Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;125(1-2):171-82. doi: 10.1007/s00418-005-0074-0. Epub 2005 Oct 28. Histochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16261331
-
Inhibition of galectins in cancer: Biological challenges for their clinical application.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1104625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1104625. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36703969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharp P.A. (1994) Split genes and RNA splicing. Cell, 77, 805–815. - PubMed
-
- Kramer A. (1996) The structure and function of proteins involved in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 65, 367–409. - PubMed
-
- Reed R. (2000) Mechanisms of fidelity in pre-mRNA splicing. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12, 340–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

