Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect
- PMID: 11523746
- PMCID: PMC2819361
- DOI: 10.1023/a:1026595011371
Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect
Abstract
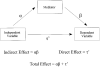
This paper describes the statistical similarities among mediation, confounding, and suppression. Each is quantified by measuring the change in the relationship between an independent and a dependent variable after adding a third variable to the analysis. Mediation and confounding are identical statistically and can be distinguished only on conceptual grounds. Methods to determine the confidence intervals for confounding and suppression effects are proposed based on methods developed for mediated effects. Although the statistical estimation of effects and standard errors is the same, there are important conceptual differences among the three types of effects.
References
-
- Ajzen I, Fishbein M. Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Prentice Hall; Englewood Cliffs, NJ: 1980.
-
- Alwin DF, Hauser RM. The decomposition of effects in path analysis. American Sociological Review. 1975;40:37–47.
-
- Aroian LA. The probability function of the product of two normally distributed variables. Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 1944;18:265–271.
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bobko P, Rieck A. Large sample estimators for standard errors of functions of correlation coefficients. Applied Psychological Measurement. 1980;4:385–398.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources