Direct incorporation of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine into exopolymers by Gluconacetobacter xylinus (=Acetobacter xylinum) ATCC 10245: production of chitosan-cellulose and chitin-cellulose exopolymers
- PMID: 11525993
- PMCID: PMC93117
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.3970-3975.2001
Direct incorporation of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine into exopolymers by Gluconacetobacter xylinus (=Acetobacter xylinum) ATCC 10245: production of chitosan-cellulose and chitin-cellulose exopolymers
Abstract
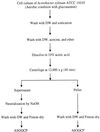
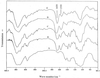
Gluconacetobacter xylinus (=Acetobacter xylinum) ATCC 10245 incorporated 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose (glucosamine) and 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose (N-acetylglucosamine), but not 3-O-methyl-D-glucose or 2-deoxy-D-glucose into exopolymers. Incorporation was confirmed by gas chromatography with and without mass spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared, and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. The average molar percentage of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine in the exopolymers was about 18%.
Figures



References
-
- Aiba S. Studies on chitosan. 2. Solution stability and reactivity of partially N-acetylated chitosan derivatives in aqueous media. Int J Biol Macromol. 1989;11:249–252. - PubMed
-
- Anthonsen M W, Vårum K M, Smidsrød O. Solution properties of chitosan: conformation and chain stiffness of chitosans with different degrees of N-acetylation. Carbohydr Polym. 1993;22:193–201.
-
- Arcidiacono S, Kaplan D L. Molecular weight distribution of chitosan isolated from Mucor rouxii under different culture and processing conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1992;39:281–286. - PubMed
-
- Canale-Parola E, Wolfe R S. Synthesis of cellulose by Sarcina ventriculi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964;82:403–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

