Diversity of Babesia Infecting European sheep ticks (Ixodes ricinus)
- PMID: 11526189
- PMCID: PMC88357
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.9.3395-3397.2001
Diversity of Babesia Infecting European sheep ticks (Ixodes ricinus)
Abstract
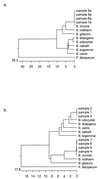
Questing Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) adult and nymphal ticks collected in various parts of Slovenia were tested for the presence of babesial parasites with a PCR assay based on the nuclear small subunit rRNA gene (nss-ribosomal DNA [rDNA]). Thirteen of 135 ticks were found to contain babesial DNA. Sequence determination and analysis of amplified portions of nss-rDNA revealed their identity with Babesia microti and a high degree of homology with Babesia odocoilei and Babesia divergens. The results of this study represent the first genetic evidence of B. microti and B. divergens-like parasites in I. ricinus ticks in Europe.
Figures
References
-
- Allsopp M T, Cavalier-Smith T, De Waal D T, Allsopp B A. Phylogeny and evolution of the piroplasms. Parasitology. 1994;108:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong P M, Katavolos P, Caporale D A, Smith R P, Spielman A, Telford S R. Diversity of Babesia infecting deer ticks (Ixodes dammini) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;58:739–742. - PubMed
-
- Gorenflot A, Moubri K, Precigout E, Carcy B, Schetters T P. Human babesiosis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1998;92:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Healing T D. Infections with blood parasites in the small British rodents Apodemus sylvaticus, Clethrionomys glareolus and Microtus agrestis. Parasitology. 1981;83:179–189. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

