Induction of CD4(+) T cell-dependent CD8(+) type 1 responses in humans by a malaria DNA vaccine
- PMID: 11526203
- PMCID: PMC58557
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.181123498
Induction of CD4(+) T cell-dependent CD8(+) type 1 responses in humans by a malaria DNA vaccine
Abstract
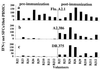
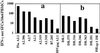
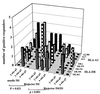
We assessed immunogenicity of a malaria DNA vaccine administered by needle i.m. or needleless jet injection [i.m. or i.m./intradermally (i.d.)] in 14 volunteers. Antigen-specific IFN-gamma responses were detected by enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assays in all subjects to multiple 9- to 23-aa peptides containing class I and/or class II restricted epitopes, and were dependent on both CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells. Overall, frequency of response was significantly greater after i.m. jet injection. CD8(+)-dependent cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) were detected in 8/14 volunteers. Demonstration in humans of elicitation of the class I restricted IFN-gamma responses we believe necessary for protection against the liver stage of malaria parasites brings us closer to an effective malaria vaccine.
Figures
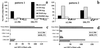
References
-
- Hoffman S L, Franke E D, Hollingdale M R, Druilhe P. In: Malaria Vaccine Development. Hoffman S L, editor. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1996. pp. 35–75.
-
- Hoffman S L. In: MIM Africa Malaria Conference. Sharp B, Davies K, editors. Multilateral Initiative on Malaria; 1999. pp. 145–152.
-
- Doolan D L, Hoffman S L. Parasitol Today. 1997;13:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman S L, Doolan D L. In: Developments and Clinical Progress of DNA Vaccines. Brown F, Cichutek K, Robertson J, editors. Vol. 104. Basel: Karger; 2000. pp. 121–132.
-
- Wang R, Doolan D L, Le T P, Hedstrom R C, Coonan K M, Charoenvit Y, Jones T R, Hobart P, Margalith M, Ng J, et al. Science. 1998;282:476–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

