Increased distribution and expression of CD64 on blood polymorphonuclear cells from patients with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
- PMID: 11529918
- PMCID: PMC1906134
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01596.x
Increased distribution and expression of CD64 on blood polymorphonuclear cells from patients with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Abstract
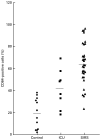
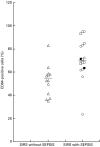
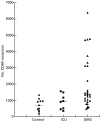
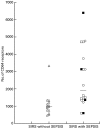
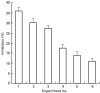
Evidence is growing to suggest that the multiple organ damage of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) arises from the untoward activity of blood polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), which upon activation acquire the IgG high affinity receptor, CD64. In the current study, flow cytometry was used to assess the prevalence of CD64-bearing PMNs and the intensity of expression of CD64 in whole blood samples from 32 SIRS patients, 11 healthy normal subjects and from eight non-SIRS patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). The percentage of PMNs expressing CD64 was higher in SIRS patients (mean 65%) than in non-SIRS patients (mean 42%; P < 0.02) and in healthy controls (mean 19%; P < 0.001) and was particularly evident in patients with SIRS and sepsis (mean 71%; P < 0.02) as opposed to SIRS alone (mean 55%). There were more CD64 molecules expressed on PMNs from patients with SIRS (median 1331 molecules/cell) in comparison with PMNs from healthy subjects (median 678 molecules/cell; P < 0.01). The highest intensity of CD64 expression was associated with PMNs from patients with both SIRS and sepsis. Functional studies revealed that the supranormal binding of PMNs from patients with SIRS to endothelial monolayers treated with TNFalpha was impeded by anti-CD64 antibodies (mean 24% inhibition; P < 0.01). Monitoring the distribution of CD64+ PMNs and their level of CD64 expression could be of assistance in the rapid discrimination of patients with SIRS from other ICU patients and in the identification of PMNs which are likely to participate in the pathological manifestations of the disease.
Figures
References
-
- Schoenberg MH, Weiss M, Radermacher P. Outcome of patients with sepsis and septic shock after ICU treatment. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 1998;383:44–8. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra RB, et al. Definition for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–55. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC. Immunologic dissonance: a continuing evolution in our understanding of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) Ann Int Med. 1993;125:680–7. - PubMed
-
- Parillo JE. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1471–7. - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Boissin C, Haccoun M, Thomachot L, Mege JL. Patterns of cytokine evolution (tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6) after septic shock, haemorrhagic shock, and severe trauma. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:1813–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

