A snapshot of waiting times for cancer surgery provided by surgeons affiliated with regional cancer centres in Ontario
- PMID: 11531050
- PMCID: PMC81366
A snapshot of waiting times for cancer surgery provided by surgeons affiliated with regional cancer centres in Ontario
Abstract
Background: There is evidence that delays in treatment result in increased psychosocial morbidity for patients diagnosed with cancer. We evaluated waiting times for care among cancer patients treated by surgeons affiliated with regional cancer centres in Ontario.
Methods: Dates for 5 key events related to the surgical management of a patient with cancer were collected by a convenience sample of surgeons who treat breast, gynecologic, colorectal, head and neck, thoracic and urologic cancers. The key events were initial referral, first surgical visit, main treatment decision, major surgery and receipt of postoperative pathology report. The surgeons were also asked to judge the appropriateness of the waiting times for the intervals studied and to identify factors associated with inappropriate delays.
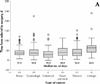
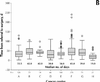
Results: A total of 62 surgeons affiliated with 8 regional cancer centres participated; data were collected for 1456 patients who underwent assessment and whose surgical visit occurred between Jan. 31 and May 31, 2000. The median waiting time from referral to first visit was 11.0 days, from first visit to treatment decision 0.0 days, from treatment decision to surgery 20.0 days and from surgery to receipt of the pathology report 8.0 days. The median waiting times for the 2 summary intervals (referral to surgery and referral to receipt of the pathology report) were 37.0 and 48.0 days respectively. The waiting times varied by cancer type; for example, the median time from referral to surgery varied from 29.0 days for colorectal cancers to 64.0 days for urologic cancers. The same interval varied from 19.0 to 43.0 days by treatment centre. The waiting times did not vary substantially by patient age. The surgeons judged that 344 (37.2%) of the 925 patients with dates for the referral-to-surgery interval had inappropriately long waiting times. They indicated that contributing factors to these inappropriate waits were shortage of operating room time (in 181 cases), lack of other resources such as diagnostic tests or allied health personnel (in 156) and patient preference or circumstance (in 28) (factors were not mutually exclusive).
Interpretation: Many of the patients with cancer seen by surgeons affiliated with regional cancer centres in Ontario may be experiencing significant delays in the assessment and treatment of their cancer.
Figures
Comment in
-
Waiting times for cancer surgery.CMAJ. 2002 Mar 19;166(6):710; author reply 710-1. CMAJ. 2002. PMID: 11944754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Canadian Society for Surgical Oncology position statement. Available: www.cos.ca/csso/policy.htm (accessed 2001 July 10).
-
- Draft synthesis report. Canadian Strategy for Cancer Control; 2001 Jan 18. Available: www.hc-sc.gc.ca/hppb/cscc/work_reports.html (accessed 2001 July 10).
-
- Benedict S, Williams RD, Baron PL. Recalled anxiety: from discovery to diagnosis of a benign breast mass. Oncol Nurs Forum 1994;21(10):1723-7. - PubMed
-
- Risberg T, Sorbye SW, Norum J, Wist EA. Diagnostic delay causes more psychological distress in female than in male breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res 1996;16(2):995-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
