Invertebrate connectin spans as much as 3.5 microm in the giant sarcomeres of crayfish claw muscle
- PMID: 11532946
- PMCID: PMC125597
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4826
Invertebrate connectin spans as much as 3.5 microm in the giant sarcomeres of crayfish claw muscle
Abstract
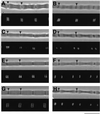
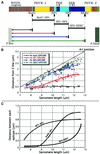
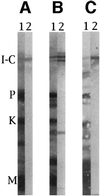
In crayfish claw closer muscle, the giant sarcomeres are 8.3 microm long at rest, four times longer than vertebrate striated muscle sarcomeres, and they are extensible up to 13 microm upon stretch. Invertebrate connectin (I-connectin) is an elastic protein which holds the A band at the center of the sarcomere. The entire sequence of crayfish I-connectin was predicted from cDNA sequences of 53 424 bp (17 352 residues; 1960 kDa). Crayfish I-connectin contains two novel 68- and 71-residue repeats, and also two PEVK domains and one kettin region. Kettin is a small isoform of I-connectin. Immunoblot tests using antibody to the 68-residue repeats revealed the presence of I-connectin also in long sarcomeres of insect leg muscle and barnacle ventral muscle. Immunofluorescence microscopy demonstrated that the two repeats, the long spacer and the two PEVK domains contribute to sarcomere extension. These regions rich in charged amino acids, occupying 63% of the crayfish I-connectin molecule, may allow a span of a 3.5 microm distance as a new class of composite spring.
Figures
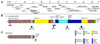




References
-
- Benian G.M., Ayme-Southgate,A. and Tinley,T.L. (1999) The genetics and molecular biology of the titin/connectin-like proteins of invertebrates. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 138, 235–268. - PubMed
-
- Daley J., Southgate,R. and Ayme-Southgate,A. (1998) Structure of the Drosophila projectin protein: isoforms and implication for projectin filament assembly. J. Mol. Biol., 279, 201–210. - PubMed
-
- Endo T. and Nadal-Ginard,B. (1987) Three types of muscle-specific gene expression in fusion-blocked rat skeletal muscle cells: translational control in EGTA-treated cells. Cell, 49, 515–526. - PubMed
-
- Freiburg A. et al. (2000) Series of exon-skipping events in the elastic spring region of titin as the structural basis for myofibrillar elastic diversity. Circ. Res., 86, 1114–1121. - PubMed
-
- Gautel M., Mues,A. and Young,P. (1999) Control of sarcomeric assembly: the flow of information on titin. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 138, 97–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

