Deregulated beta-catenin induces a p53- and ARF-dependent growth arrest and cooperates with Ras in transformation
- PMID: 11532955
- PMCID: PMC125598
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4912
Deregulated beta-catenin induces a p53- and ARF-dependent growth arrest and cooperates with Ras in transformation
Abstract
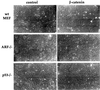
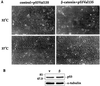
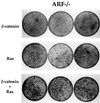
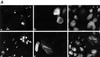
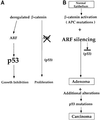
Aberrant activation of beta-catenin contributes to the onset of a variety of tumors. We report that a tumor-derived beta-catenin mutant induces accumulation and activation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Induction is mediated through ARF, an alternative reading frame product of the INK4A tumor suppressor locus, in a manner partially dependent on the transcription factor E2F1. In wild-type mouse embryo fibroblasts, mutant beta-catenin inhibits cell proliferation and imposes a senescence-like phenotype. This does not occur in cells lacking either ARF or p53, where deregulated beta-catenin actually overrides density-dependent growth inhibition and cooperates with activated Ras in transformation. Thus, the oncogenic activity of deregulated beta-catenin is curtailed by concurrent activation of the p53 pathway, thereby providing a protective mechanism against cancer. When the p53 pathway is impaired, deregulated beta-catenin is free to manifest its oncogenic features. This can occur not only by p53 mutations, but also by ablation of ARF expression, as observed frequently in early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis.
Figures






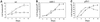


References
-
- Bates S., Phillips,A.C., Clark,P.A., Stott,F., Peters,G., Ludwig,R.L. and Vousden,K.H. (1998) p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature, 395, 124–125. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J., von Kries,J.P., Kuhl,M., Bruhn,L., Wedlich,D., Grosschedl, R. and Birchmeier,W. (1996) Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature, 382, 638–642. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J., Jerchow,B.A., Wurtele,M., Grimm,J., Asbrand,C., Wirtz,R., Kuhl,M., Wedlich,D. and Birchmeier,W. (1998) Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with β-catenin, APC and GSK3β. Science, 280, 596–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

